The different operators in SQL
An SQL operator is a special word or character used to perform tasks like addition, subtraction, division, modulus, comparison, etc. There are different types of SQL operators
Arithmetic Operators are used for addition(+),subtraction(-),multiplication(*), division(/).
Addition
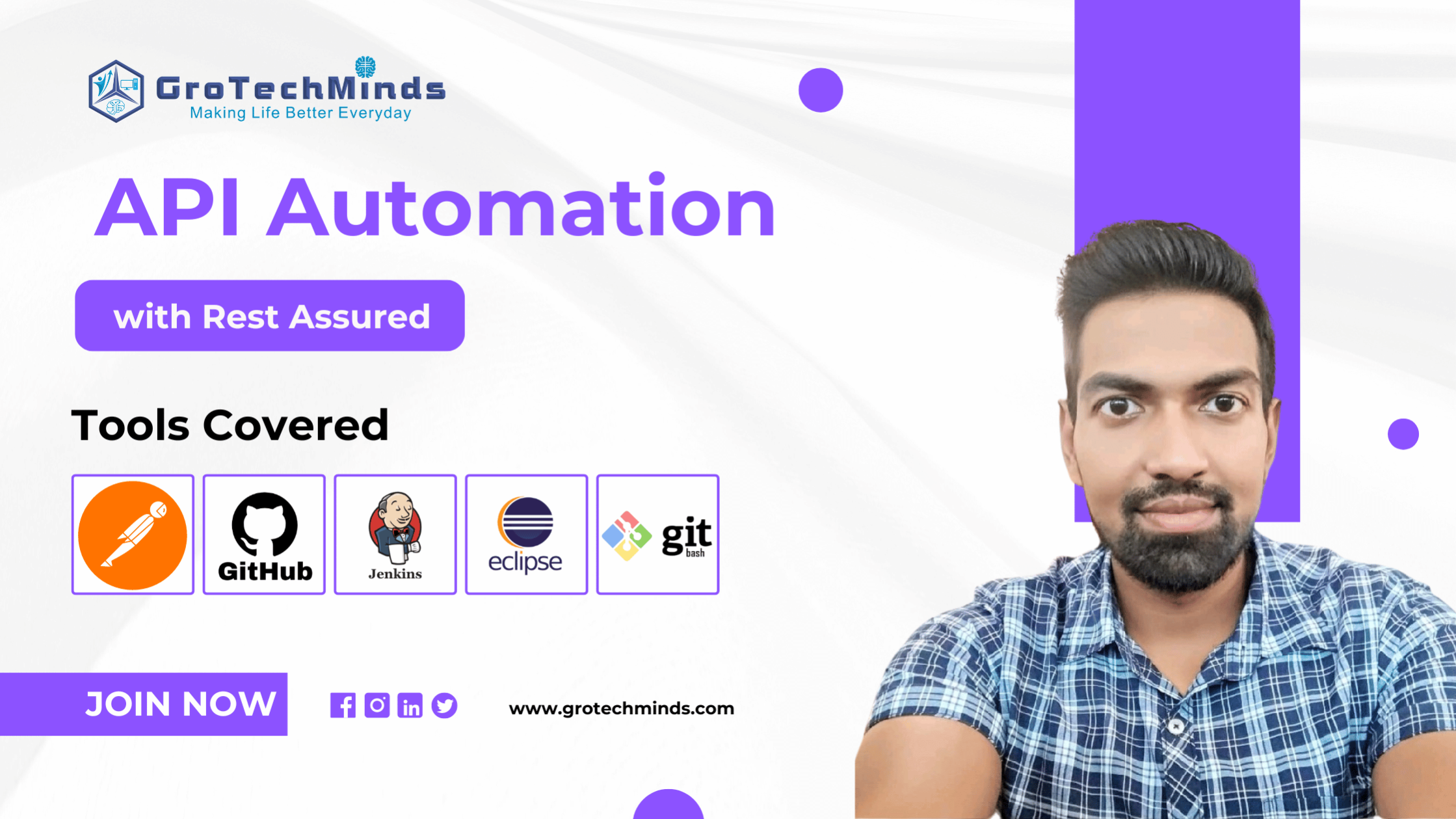
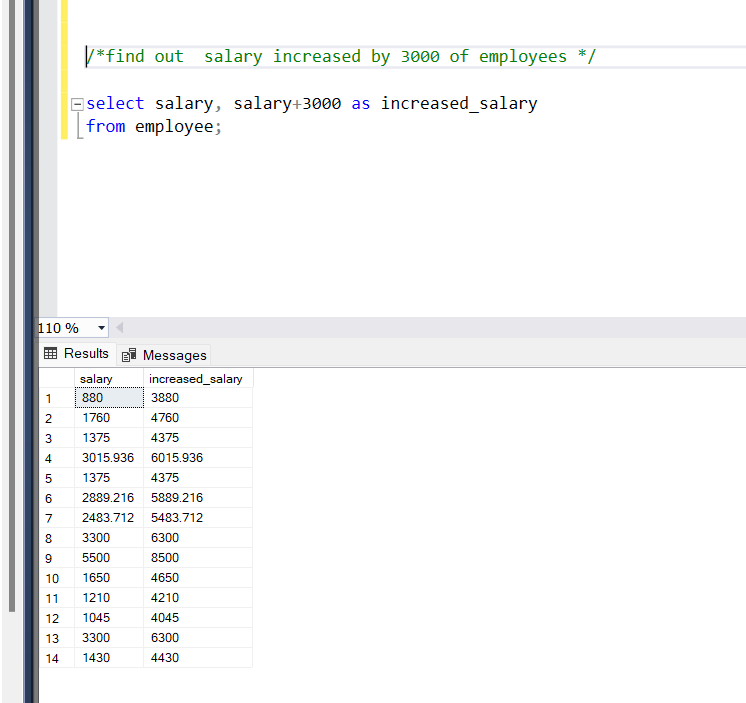
We can add columns and get the result. As in the below example we can find the monthly salary by using literals, any value we are using in the query can be done by using ‘ +’ and If we want to modify something in the column name as they vanish, that’s the reason the new column is given as increased_salary.
Problem Statement:
Find out salary and salary increased by 3000 of employees
Query:
select salary, salary+3000 as increased_salary
from employee;
We can subtract columns and get the result. As in the below example we can find the monthly salary by using literals, any value we are using in the query can be done by using ‘ -’ and If we want to modify something in the column name as they vanish, that’s the reason the new column is given as decreased_salary.
Problem Statement:
Find out salary and salary decreased by 300 of employees
Query:
select salary, salary-300 as decreased_salary
from employee;
We can multiply columns and get the result. As in the below example we can find the yearly salary by using literals any value we are using in the query can be done by using ‘ *’ and If we want to modify something in the column name as they vanish, that’s the reason the new column is given as yearly_salary.
Problem Statement:
Find out the salary and monthly salary of employees
Query:
select salary, salary*12 as monthy_salary
from employee;
We can divide columns and get the result. As in the below example we can find the per day salary by using literals, any value we are using in the query can be done by using ‘ /’, and If we want to modify something in the column name as they vanish, that’s the reason the new column is given as perday_salary.
Problem Statement:
Find out the salary and per day salary of employees
Query:
select salary, salary/30 as perday_salary
from employee;
Conditional Operators are greater than(>),smaller than(<),greater than or equals to(>=),smaller than or equals to(<=),assisgnment(=),comparison(==),not equals to(<> or !=)
- Operator greater than(>)
In this ‘>’ operator we get values greater than the value given.
Problem Statement:
Find out those employees who have a salary greater than 2000
Query:
select ename,salary
from employee
where salary>2000;
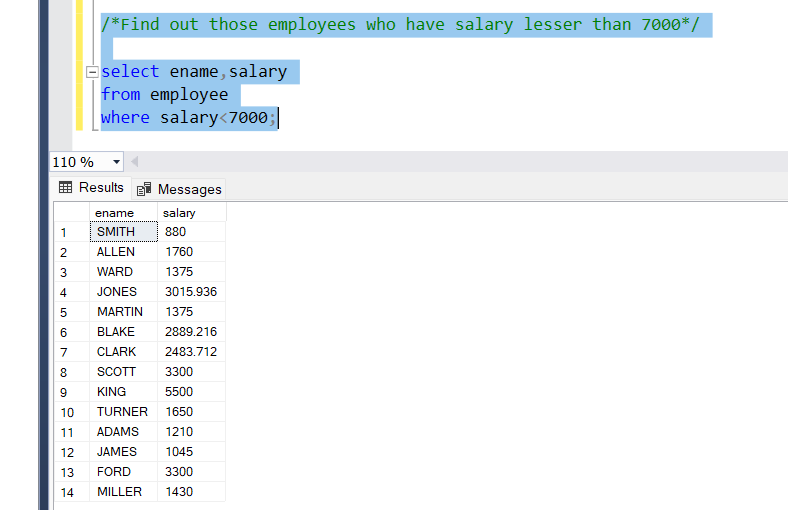
- Operator lesser than(<)
The ‘<’ operator we can get those values that are lesser than the value given.
Problem Statement:
Find out those employees who have salaries less than 7000
Query:
select ename,salary
from employee
where salary<7000;
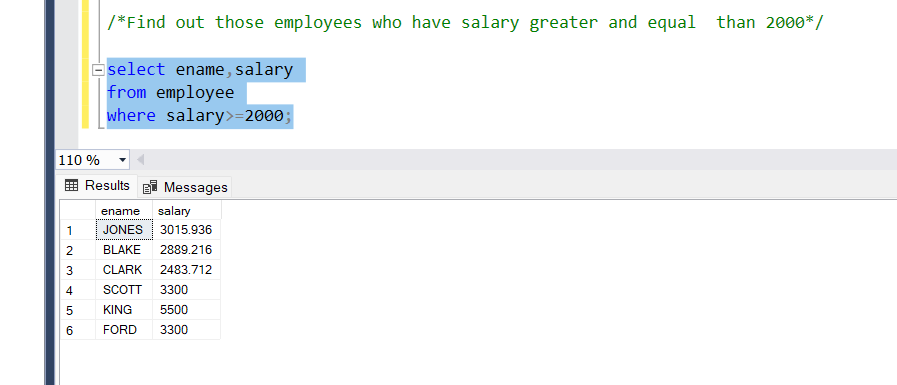
- Operator greater than(>=)
The’ >=’ operator we can get values greater and equal to the value given.
Problem Statement:
Find out those employees who have salaries greater than and equal to 2000
Query:
select ename,salary
from employee
where salary>=2000;
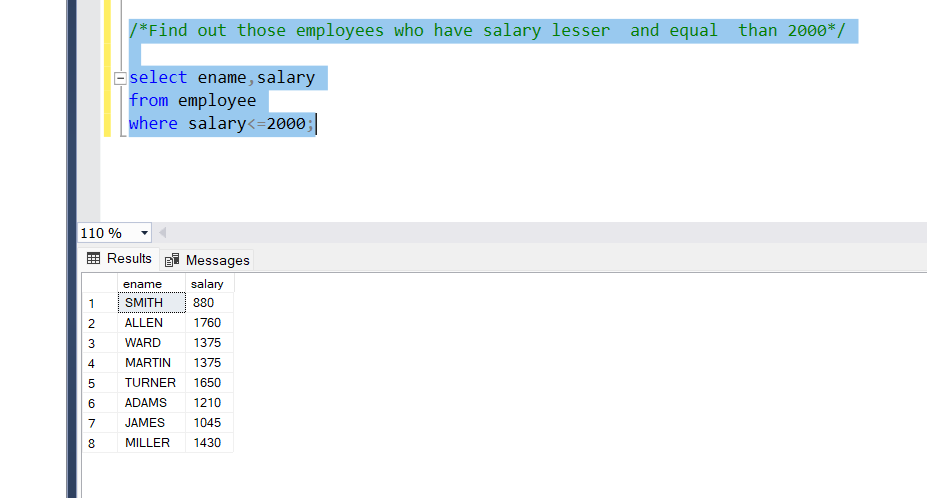
- Operator lesser than(<=)
The ‘<=’ operator we can get those values that are lesser and equal to the value given.
Problem Statement;
Find out those employees who have a salary lesser than and equal to 2000
Query:
select ename,salary
from employee
where salary<=2000;
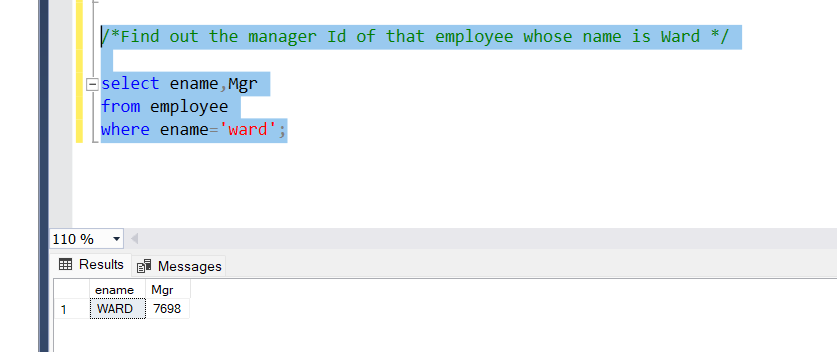
- Assignment Operator (=)
The ‘ =’ operator we assign values from right to left.
Problem Statement:
Find out the manager ID of that employee whose name is Ward.
Query:
select ename,Mgr
from employee
where ename=’ward’;
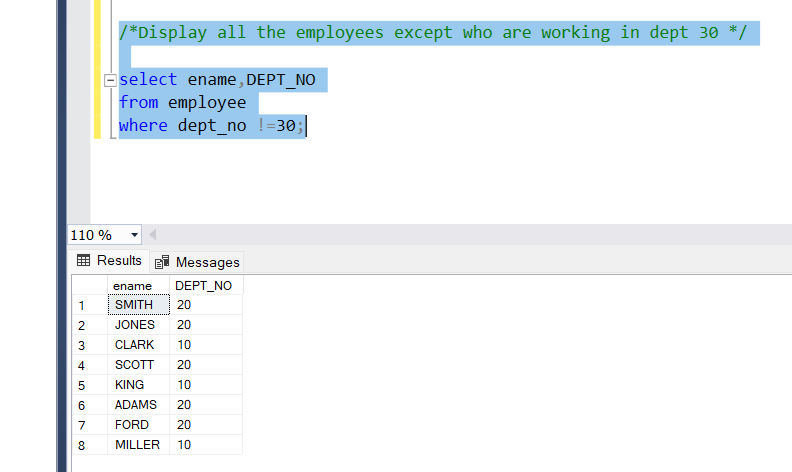
- Not Equals to Operator (!=)
The ‘!=’ operator we find a value that is not equal to.
Problem Statement:
Display all the employees except those who are working in dept 30
Query:
select ename,DEPT_NO
from employee
where dept_no !=30;
Logical operators are ‘And’, ‘Or’
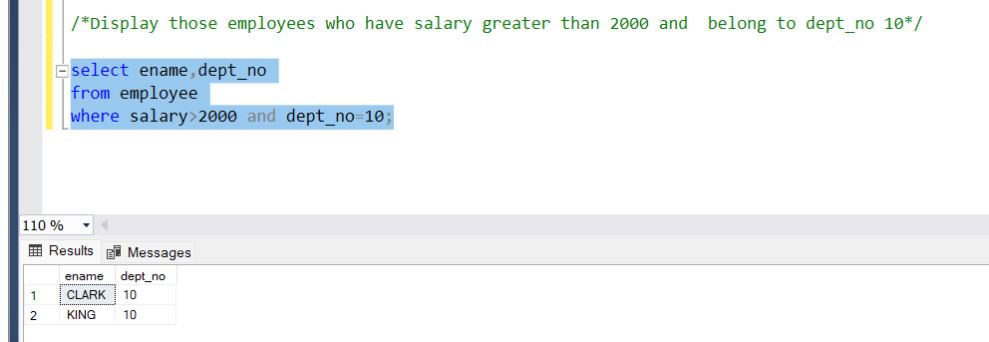
- And Operator
The ‘and’ operator, if both conditions are True, only it will display the output.
Problem Statement:
Display those employees who have a salary greater than 2000 and belong to dept_no 10
Query:
select ename,dept_no
from employee
where salary>2000 and dept_no=10;
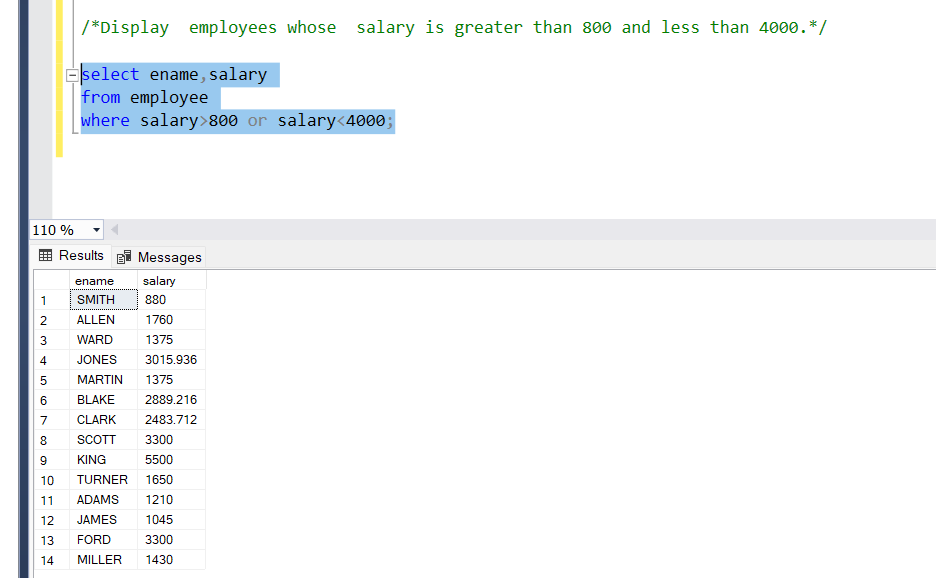
- OR Operator
The ‘or’ operator, if either of the conditions is True, will display output.
Problem Statement:
Display employees whose salary is greater than 800 and less than 4000.
Query:
select ename,salary
from employee
where salary>800 or salary<4000;
- Special Operators
Special operators are ‘Like’,; is’, ‘in’, and ‘between’.
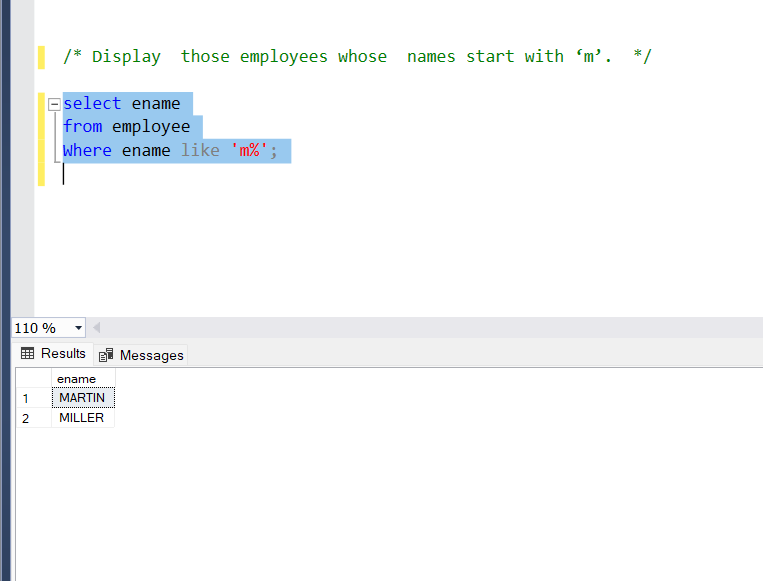
like operator
The ‘like’ operator searches single characters or multicharacter searches.
a)Multicharacter search- We search by using ‘%’.
Problem Statement:
Display those employees whose names start with ‘m’.
Query:
select ename
from employee
Where ename like ‘m%’;
b) Single character search- We search by using ‘_’.
Problem Statement:
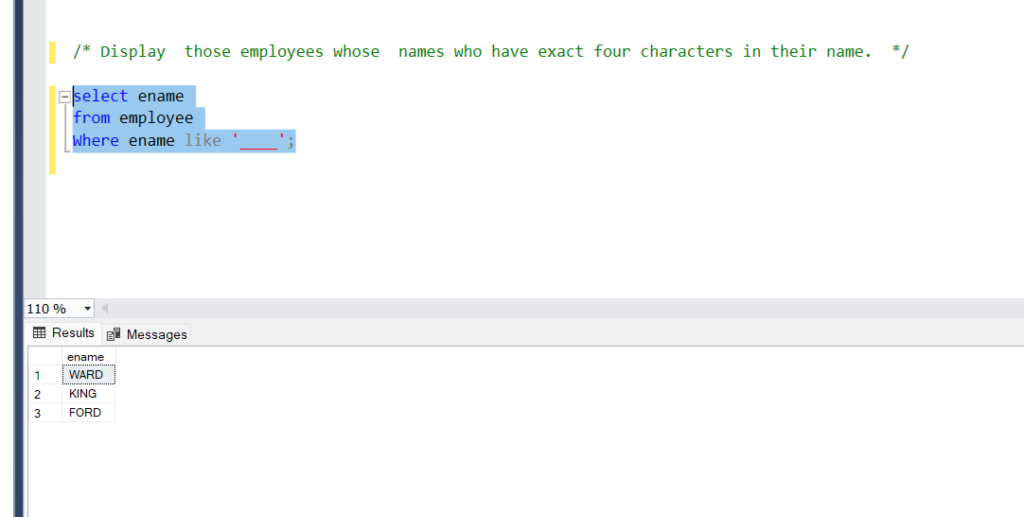
Display those employees whose names have exactly four characters in their name.
Query:
select ename
from employee
Where ename like ‘____’;
2) ls operator
The ‘Is’ operator is used to compare null values.
Problem Statement:
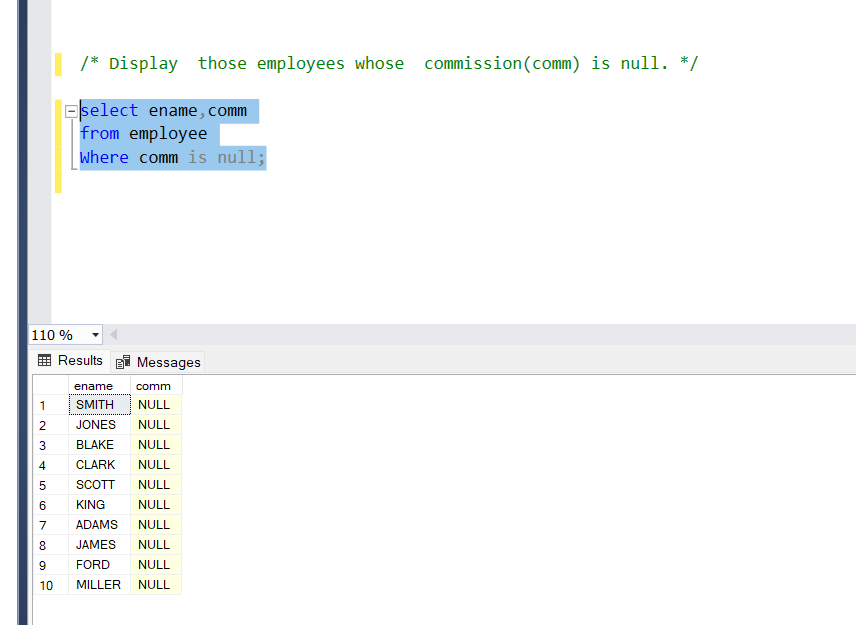
Display those employees whose commission(comm) is null.
Query:
select ename, comm
from employee
Where comm is null;
3) In operator
The ‘In’ operator displays two values of the same column name together.
Problem Statement:
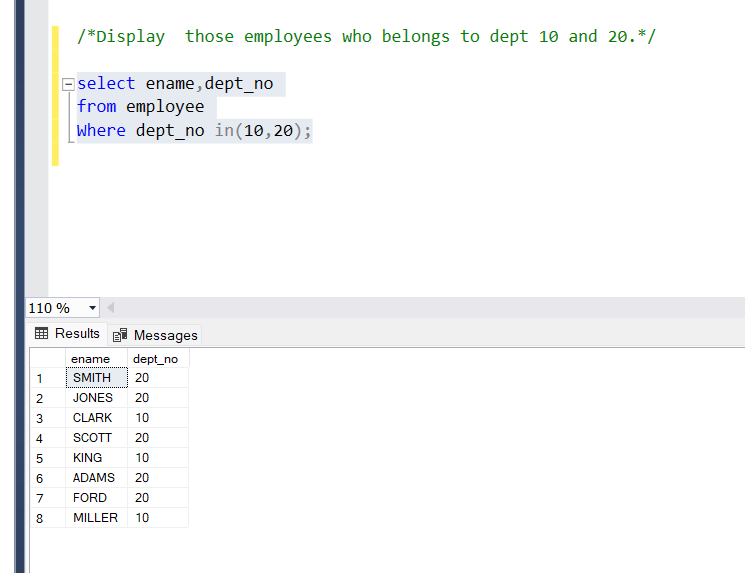
Display those employees who belong to dept 10 and 20.
Query:
select ename,dept_no
from employee
Where dept_no in(10,20);
4) between operator
The ‘between’ operator displays a range of two values between the same column name.
Problem Statement:
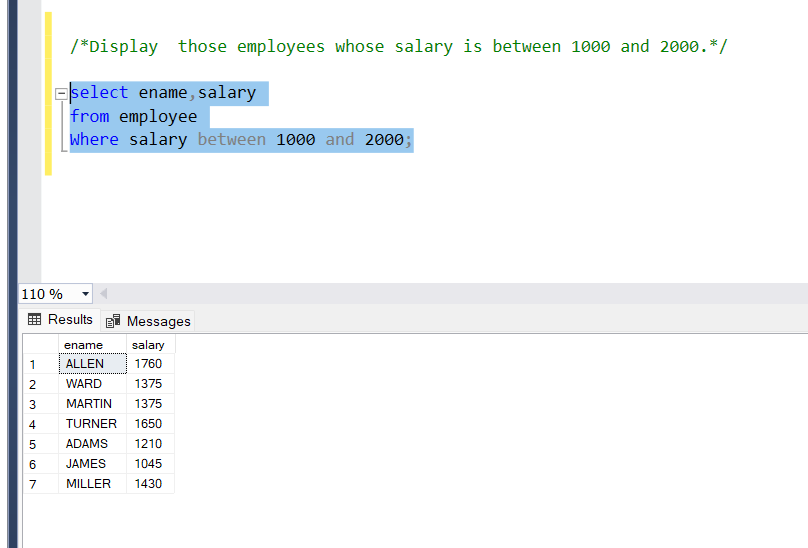
Display those employees whose salary is between 1000 and 2000.
Query:
select ename,salary
from employee
Where salary between 1000 and 2000;
- not like operator
The ‘Like not’ operator is used for searching single characters or multicharacter searches which are not required.
a)Multicharacter search- We search by ‘not like %’.
Problem Statement:
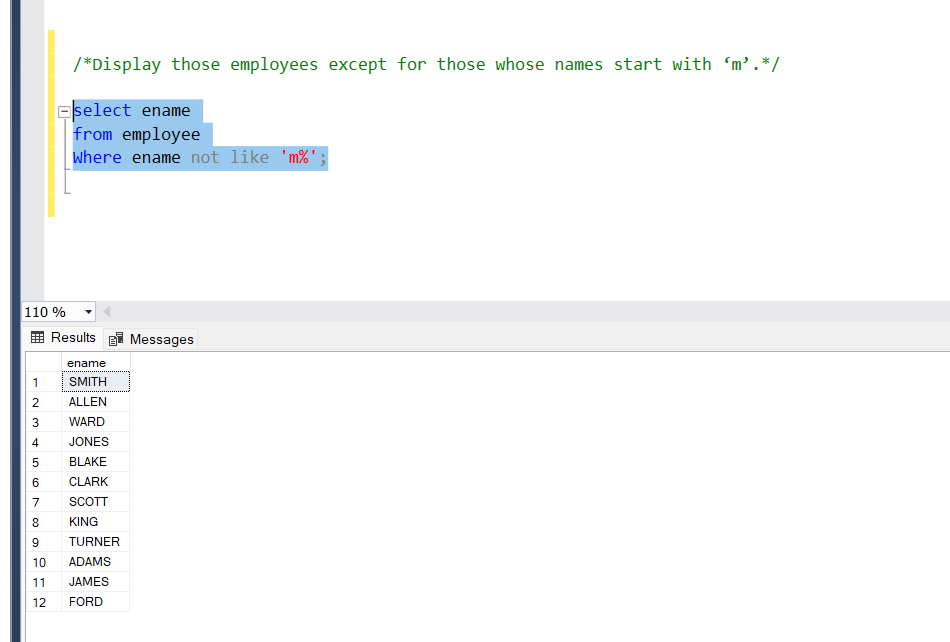
Display those employees except for those whose names start with ‘m’.
Query:
select ename
from employee
Where ename not like ‘m%’;
b) Single character search- We search by ‘ not like _’.
Problem Statement:
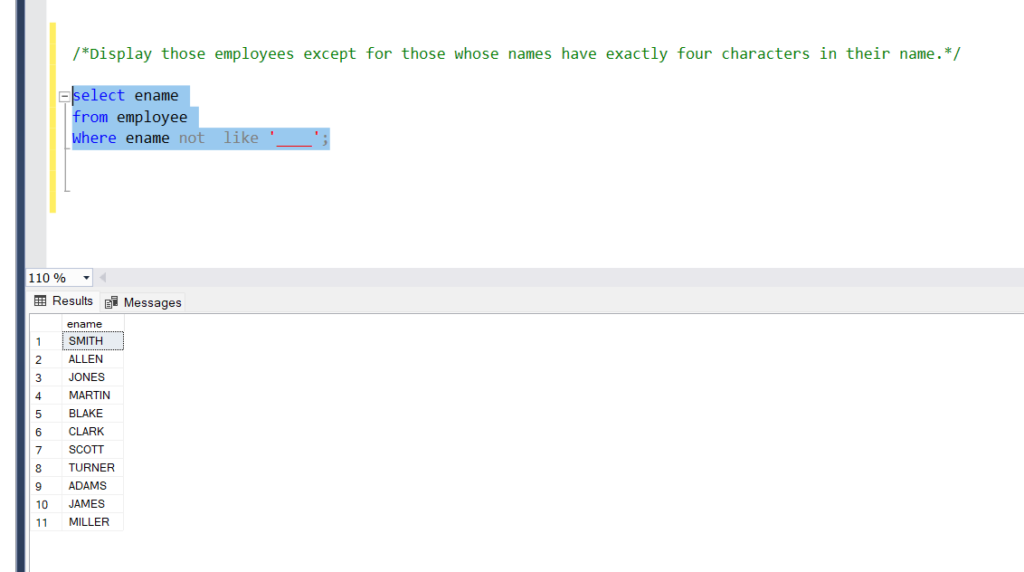
Display those employees except for those whose names have exactly four characters in their name.
Query:
select ename
from employee
Where ename not like ‘____’;
2) is not operator
The ‘Is not’ operator is used to compare not null values.
Problem Statement:
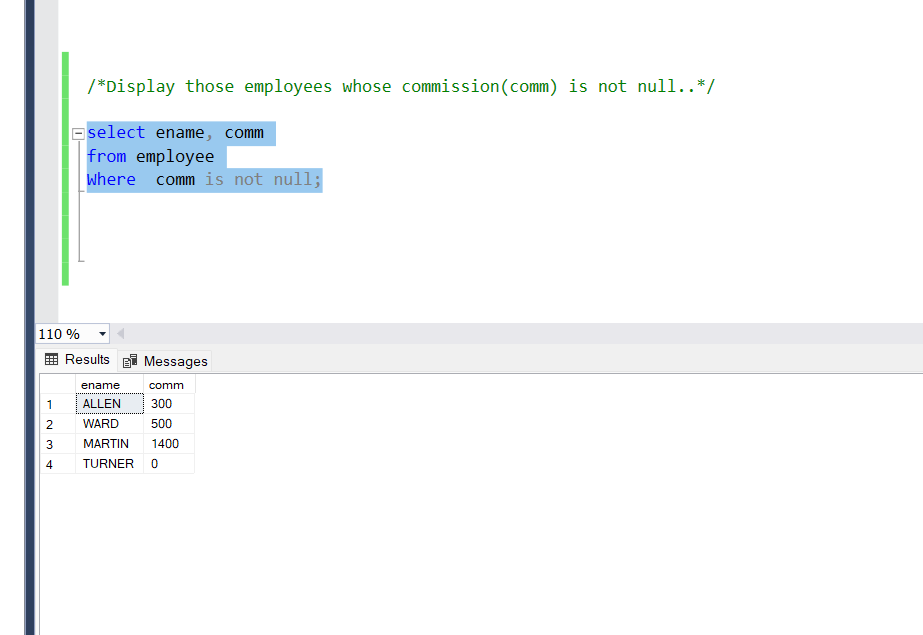
Display those employees whose commission(comm) is not null.
Query:
select ename, comm
from employee
Where comm is not null;
3) not In operator
The ‘Not In’ operator is used not to display two values of the same column name together.
Problem Statement:
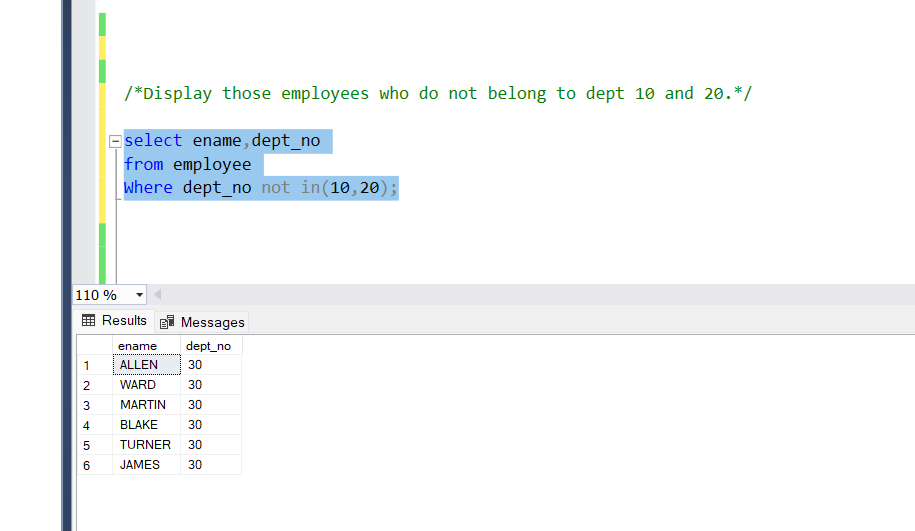
Display those employees who do not belong to dept 10 and 20.
Query:
select ename,dept_no
from employee
Where dept_no not in(10,20);
4) not between operator
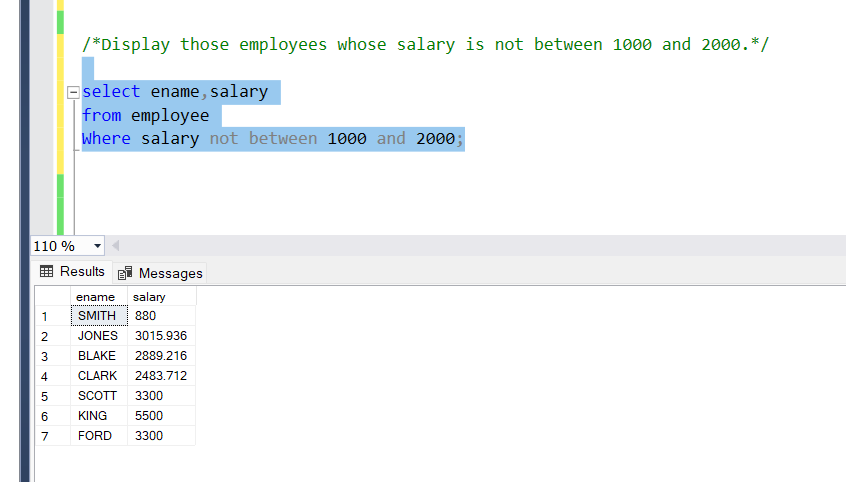
The ‘not between’ operator is not used to display a range of two values between the same column name.
Problem Statement:
Display those employees whose salary is not between 1000 and 2000.
Query:
select ename,salary
from employee
Where salary not between 1000 and 2000;
SQL operators ease the process of data manipulation. SQL operators, we can perform arithmetic, comparison, and logical operations to fetch and retrieve data from the database. Remember to practice, stay updated with the latest trends in SQL COURSE, and maintain a positive attitude throughout your interview process. We can use operators and run queries to get the desired result.
Also read:
Consult Us