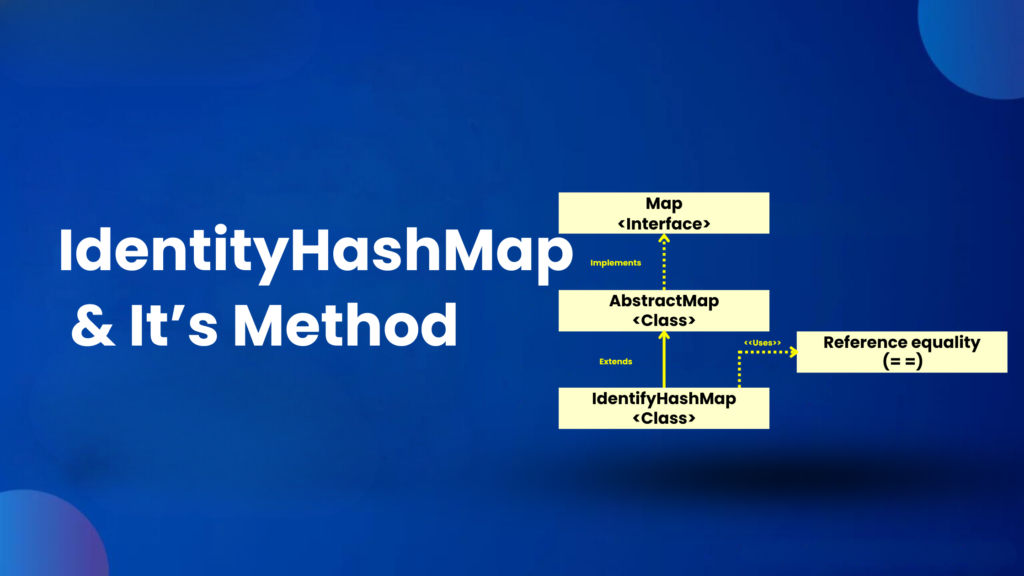
IdentityHashMap and its methods
Before going into IdentityHashMap let us discuss about Map Hierarchy
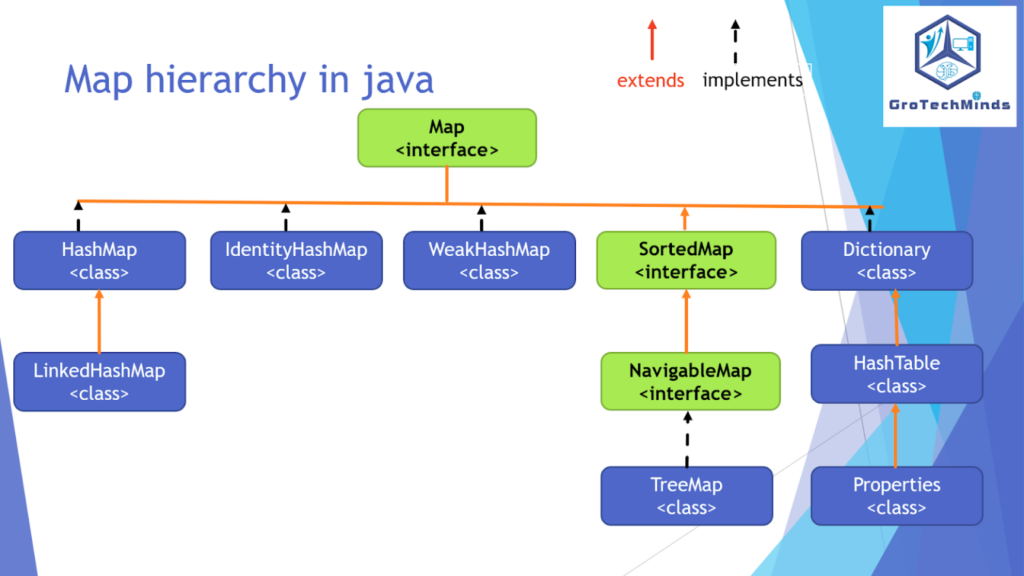
Map Hierarchy
The below diagram shows the Map hierarchy consisting of classes and interfaces.
Now let us discuss about IdentityHashMap and its methods
What is IdentityHashMap?
IdentityHashMap is the implemented class of Map interface. It uses reference equality which is called as ‘==’ operator for comparing keys and its respective values. It is present in java.utils package.It gives a constant time performance for different operations like get and put. While performing search operations it uses System.identityHashCode() method for hashing. It is neither threadsafe nor synchronized as a result it has faster execution. It increases its capacity when it reaches the load factor value of 0.75. Its threshold is 0.75 times the current capacity.
Methods of IdentityHashMap
Below are some of the methods of IdentityHashMap:
| Method Name | Description |
| put(Object key, Object value) | It is used to add a pair of key and value into the IdentityHashMap. |
| putAll(Map m) | It is used to add all pairs of keys and values from one IdentityHashMap to another IdentityHashMap. |
| clear() | It is used to clear all key and value pairs present in IdentityHashMap. |
| size() | It is used to display the size of the key and value pairs present in IdentityHashMap. |
| equals(Object o) | It is used to check if key and value pairs present in one IdentityHashMap is equal to the key and value pairs present in another IdentityHashMap. It gives ‘true’ value if key and value pairs present in two IdentityHashMaps are equal and ‘false’ value if key and value pairs present in two IdentityHashMaps are not equal. |
| containsKey(Object key) | It is used to check if the specified key is present among all the key and value pairs of IdentityHashMap class. It gives ‘true’ value if the specified Key is present among all the key and value pairs and ‘false’ value if the specified key is not present among all the key and value pairs. |
| containsValue(Object value) | It is used to check if the specified value of a key is present among all the key and value pairs of IdentityHashMap class. It gives ‘true’ value if the specified value of a key is present among all the key and value pairs and ‘false’ value if the specified value of a key is not present among all the key and value pairs. |
| get(Object key) | It is used to display the value of a specified key among all key and value pairs of HashSet. It displays ‘null’ if the specified key is not present among all key and value pairs of IdentityHashMap. |
| isEmpty() | It is used to check if the IdentityHashMap class is empty or not. It display ‘true’ value if the IdentityHashMap class is empty and ‘false’ value if the IdentityHashMap class is not empty. |
| keySet() | It is used to display the keys among all the key and value pairs present in IdentityHashMap. |
| remove(Object key) | It is used to remove a specified key and value pair from the IdentityHashMap. If we try to print a key which is not present in IdentityHashMap it will display null value but if we try to print a key which is present in IdentityHashMap it will display its corresponding value. |
| values() | It is used to display the corresponding values of the keys present in the IdentityHashMap |
| putIfAbsent(Object key, Object value) | Using this method, the specified key and value pairs get added alongwith the key and value pairs present in IdentityHashMap if that key and value pair is absent in the IdentityHashMap. If the specified key and value is present in the IdentityHashMap the specified key and value pair will not get added again in the IdentityHashMap. This method will also display the value of the specified key and value pair if that key and value pair is present in IdentityHashMap. If the specified key and value pair is not displayed in IdentityHashMap then null will be displayed. |
| replace(Object key, Object oldValue, Object newValue) | It is used to replace the old value of the specified key with a new value. Here we also mention the old value of the specified key. |
| replace(Object key, Object value) | It is used to replace the old value of the specified key with a new value. |
| entrySet() | It is used to display all the key and value pairs present in IdentityHashMap. |
| iterator() | It is used to iterate sequentially all the key and value pairs present in IdentityHashMap. |
| clone() | It is used to create a shallow copy of the key and value pairs present in IdentityHashMap. |
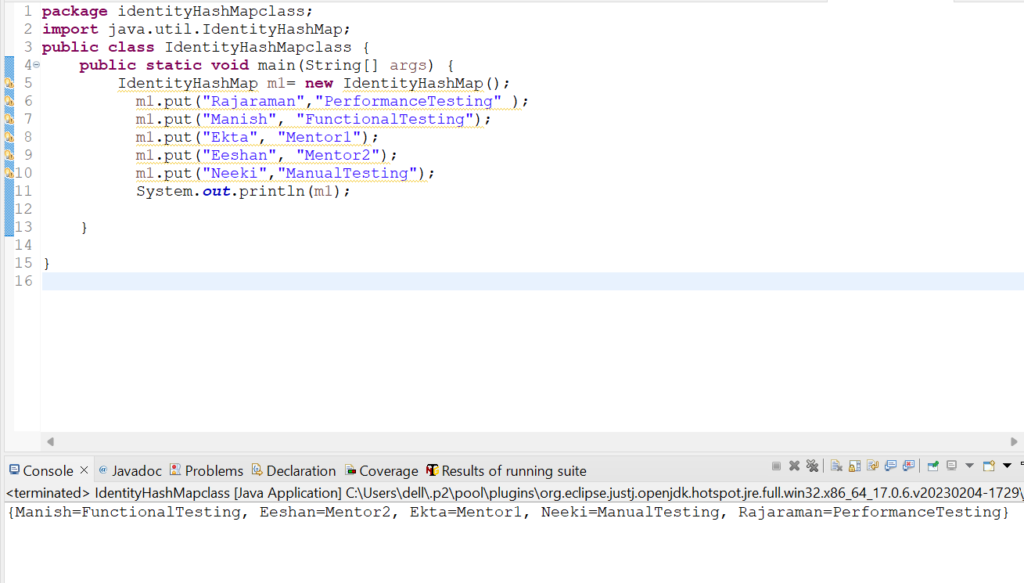
1. Let us check how put(Object key, Object value) method works in IdentityHashMap class.
Code Snippet:
package identityHashMapclass;
import java.util.IdentityHashMap;
public class IdentityHashMapclass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IdentityHashMap m1= new IdentityHashMap();
m1.put("Rajaraman","PerformanceTesting" );
m1.put("Manish", "FunctionalTesting");
m1.put("Ekta", "Mentor1");
m1.put("Eeshan", "Mentor2");
m1.put("Neeki","ManualTesting");
System.out.println(m1);
}
}
Output: {Manish=FunctionalTesting, Eeshan=Mentor2, Ekta=Mentor1, Neeki=ManualTesting, Rajaraman=PerformanceTesting}
Screenshot:
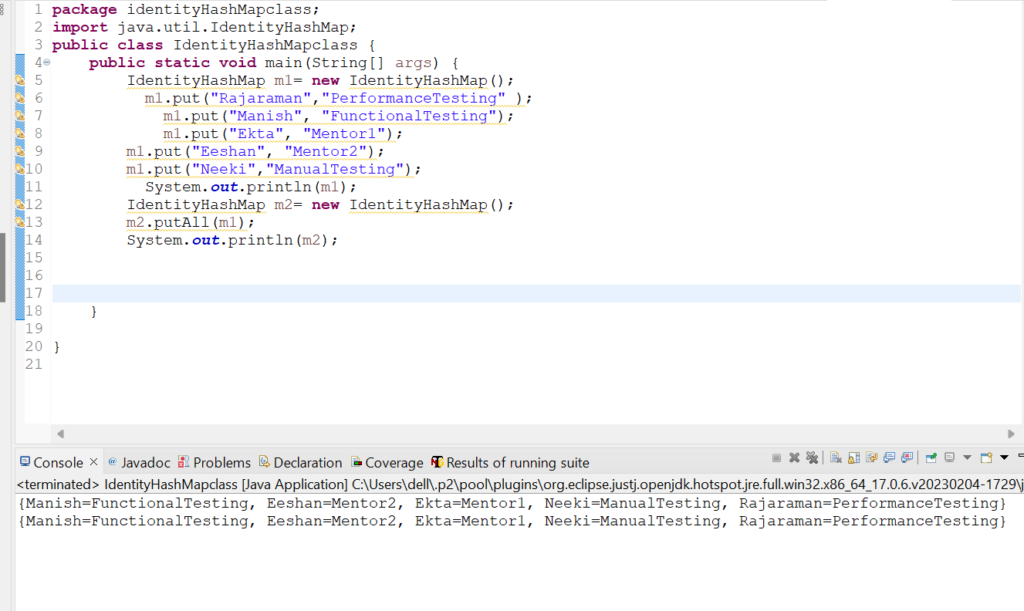
2. Let us check how putAll(Map m) method works in IdentityHashMap class.
Code Snippet:
package identityHashMapclass;
import java.util.IdentityHashMap;
public class IdentityHashMapclass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IdentityHashMap m1= new IdentityHashMap();
m1.put("Rajaraman","PerformanceTesting" );
m1.put("Manish", "FunctionalTesting");
m1.put("Ekta", "Mentor1");
m1.put("Eeshan", "Mentor2");
m1.put("Neeki","ManualTesting");
System.out.println(m1);
IdentityHashMap m2= new IdentityHashMap();
m2.putAll(m1);
System.out.println(m2);
}
}
Output: {Manish=FunctionalTesting, Eeshan=Mentor2, Ekta=Mentor1, Neeki=ManualTesting, Rajaraman=PerformanceTesting}
{Manish=FunctionalTesting, Eeshan=Mentor2, Ekta=Mentor1, Neeki=ManualTesting, Rajaraman=PerformanceTesting}
Screenshot:
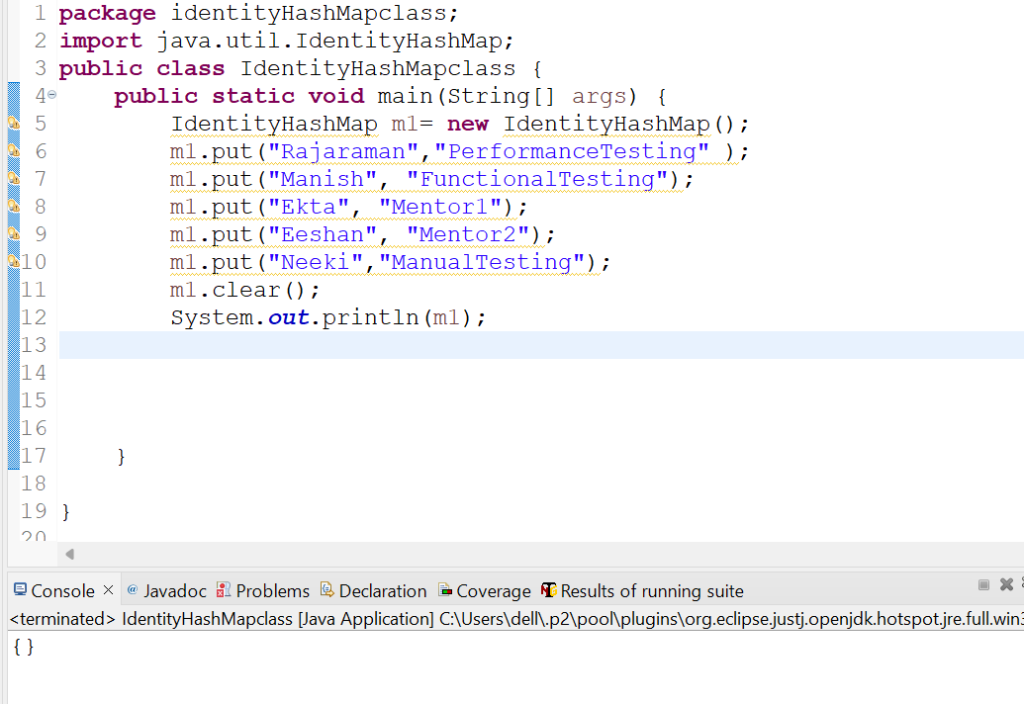
3. Let us check how clear() method works in IdentityHashMap class.
Code Snippet:
package identityHashMapclass;
import java.util.IdentityHashMap;
public class IdentityHashMapclass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IdentityHashMap m1= new IdentityHashMap();
m1.put("Rajaraman","PerformanceTesting" );
m1.put("Manish", "FunctionalTesting");
m1.put("Ekta", "Mentor1");
m1.put("Eeshan", "Mentor2");
m1.put("Neeki","ManualTesting");
m1.clear();
System.out.println(m1);
}
}
Output: {}
Screenshot:
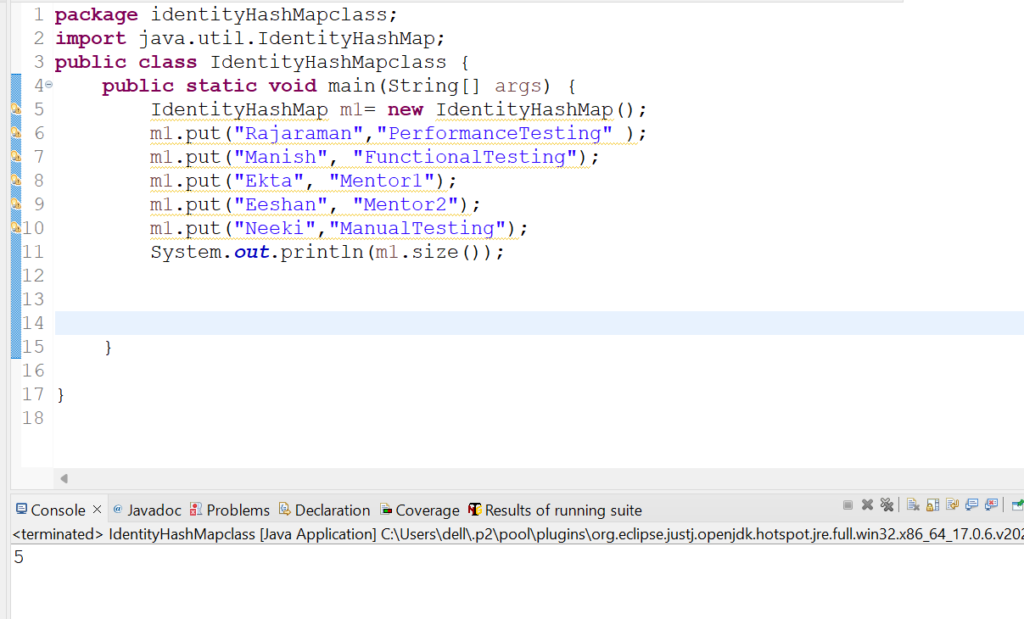
4. Let us check how size() method works in IdentityHashMap class.
Code Snippet:
package identityHashMapclass;
import java.util.IdentityHashMap;
public class IdentityHashMapclass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IdentityHashMap m1= new IdentityHashMap();
m1.put("Rajaraman","PerformanceTesting" );
m1.put("Manish", "FunctionalTesting");
m1.put("Ekta", "Mentor1");
m1.put("Eeshan", "Mentor2");
m1.put("Neeki","ManualTesting");
System.out.println(m1.size());
}
}
Output: 5
Screenshot:
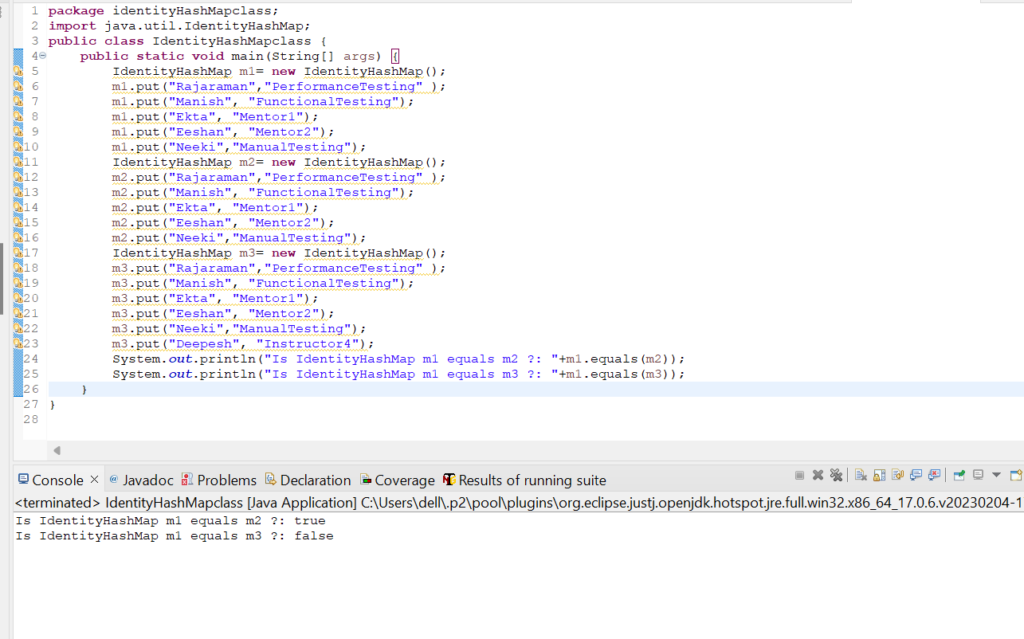
5. Let us check how equals(Object o) method works in IdentityHashMap class.
Code Snippet:
package identityHashMapclass;
import java.util.IdentityHashMap;
public class IdentityHashMapclass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IdentityHashMap m1= new IdentityHashMap();
m1.put("Rajaraman","PerformanceTesting" );
m1.put("Manish", "FunctionalTesting");
m1.put("Ekta", "Mentor1");
m1.put("Eeshan", "Mentor2");
m1.put("Neeki","ManualTesting");
IdentityHashMap m2= new IdentityHashMap();
m2.put("Rajaraman","PerformanceTesting" );
m2.put("Manish", "FunctionalTesting");
m2.put("Ekta", "Mentor1");
m2.put("Eeshan", "Mentor2");
m2.put("Neeki","ManualTesting");
IdentityHashMap m3= new IdentityHashMap();
m3.put("Rajaraman","PerformanceTesting" );
m3.put("Manish", "FunctionalTesting");
m3.put("Ekta", "Mentor1");
m3.put("Eeshan", "Mentor2");
m3.put("Neeki","ManualTesting");
m3.put("Deepesh", "Instructor4");
System.out.println("Is IdentityHashMap m1 equals m2 ?: "+m1.equals(m2));
System.out.println("Is IdentityHashMap m1 equals m3 ?: "+m1.equals(m3));
}
}
Output: Is IdentityHashMap m1 equals m2 ?: true
Is IdentityHashMap m1 equals m3 ?: false
Screenshot:
6. Let us check how containsKey(Object key) method works in IdentityHashMap class.
Code Snippet:
package identityHashMapclass;
import java.util.IdentityHashMap;
public class IdentityHashMapclass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IdentityHashMap m1= new IdentityHashMap();
m1.put("Rajaraman","PerformanceTesting" );
m1.put("Manish", "FunctionalTesting");
m1.put("Ekta", "Mentor1");
m1.put("Eeshan", "Mentor2");
m1.put("Neeki","ManualTesting");
System.out.println("Does the IdentityHashMap contains Rajaraman key?: "+m1.containsKey("Rajaraman"));
System.out.println("Does the IdentityHashMap
contains Deepesh key?: "+m1.containsKey("Deepesh"));
}
}
Output: Does the IdentityHashMap contains Rajaraman key?: true
Does the IdentityHashMap contains Deepesh key?: false
Screenshot:
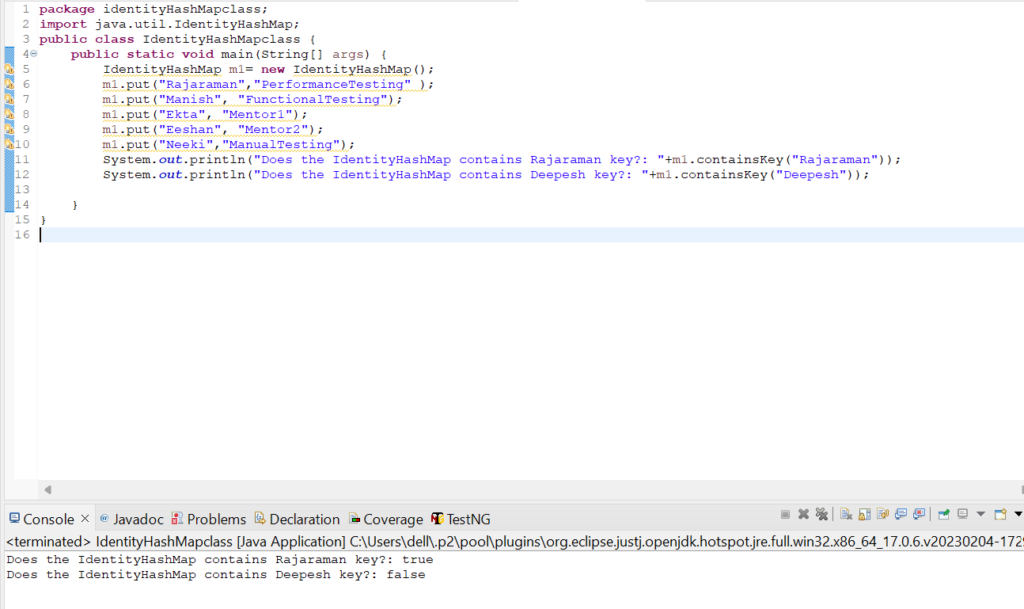
7. Let us check how containsValue(Object value) method works in IdentityHashMap class.
Code Snippet:
package identityHashMapclass;
import java.util.IdentityHashMap;
public class IdentityHashMapclass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IdentityHashMap m1= new IdentityHashMap();
m1.put("Rajaraman","PerformanceTesting" );
m1.put("Manish", "FunctionalTesting");
m1.put("Ekta", "Mentor1");
m1.put("Eeshan", "Mentor2");
m1.put("Neeki","ManualTesting");
System.out.println("Does the IdentityHashMap contains PerformanceTesting value?: "+m1.containsValue("PerformanceTesting"));
System.out.println("Does the IdentityHashMap
contains Python value?: "+m1.containsValue("Python"));
}
}
Output: Does the IdentityHashMap contains PerformanceTesting value?: true
Does the IdentityHashMap contains Python value?: false
Screenshot:
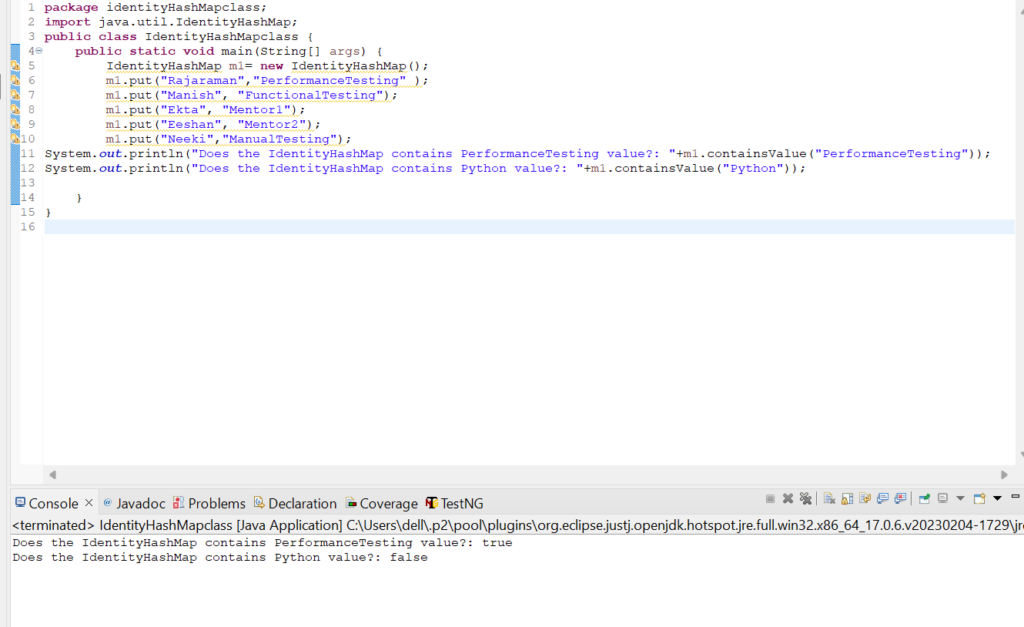
8. Let us check how get(Object key) method works in IdentityHashMap class.
Code Snippet:
package identityHashMapclass;
import java.util.IdentityHashMap;
public class IdentityHashMapclass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IdentityHashMap m1= new IdentityHashMap();
m1.put("Rajaraman","PerformanceTesting" );
m1.put("Manish", "FunctionalTesting");
m1.put("Ekta", "Mentor1");
m1.put("Eeshan", "Mentor2");
m1.put("Neeki","ManualTesting");
System.out.println(m1.get("Manish"));
System.out.println(m1.get("Deepesh"));
}
}
Output:
FunctionalTesting
null
Screenshot:
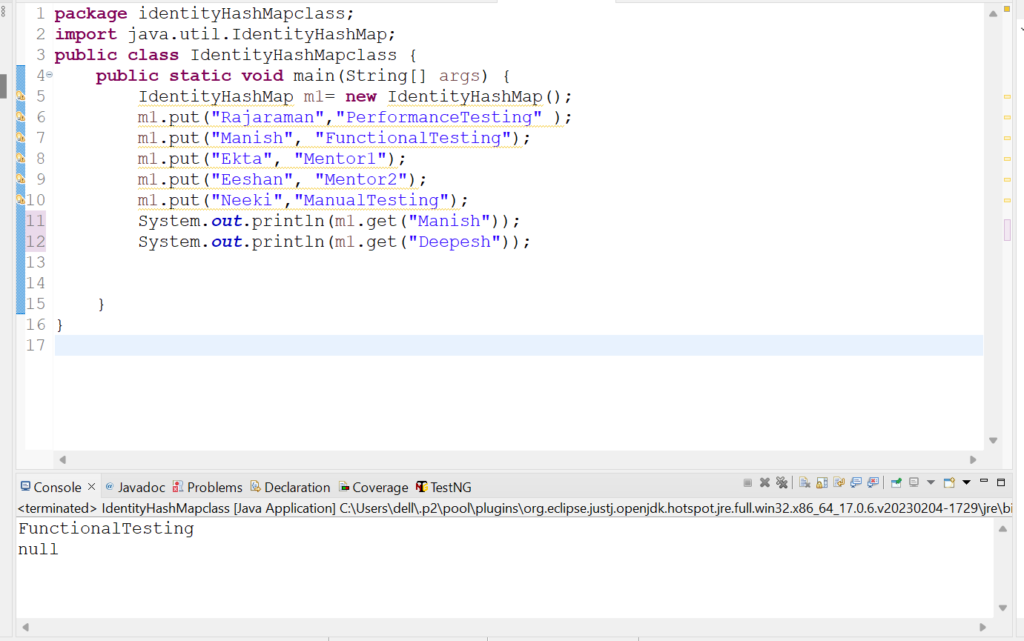
9. Let us check how isEmpty() method works in IdentityHashMap class.
Code Snippet:
package identityHashMapclass;
import java.util.IdentityHashMap;
public class IdentityHashMapclass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IdentityHashMap m1= new IdentityHashMap();
m1.put("Rajaraman","PerformanceTesting" );
m1.put("Manish", "FunctionalTesting");
m1.put("Ekta", "Mentor1");
m1.put("Eeshan", "Mentor2");
m1.put("Neeki","ManualTesting");
System.out.println("Is IdentityHashMap m1 empty? :" +m1.isEmpty());
IdentityHashMap m2= new IdentityHashMap();
System.out.println("Is IdentityHashMap m2 empty? :" +m2.isEmpty());
}
}
Output: Is IdentityHashMap m1 empty? :false
Is IdentityHashMap m2 empty? :true
Screenshot:
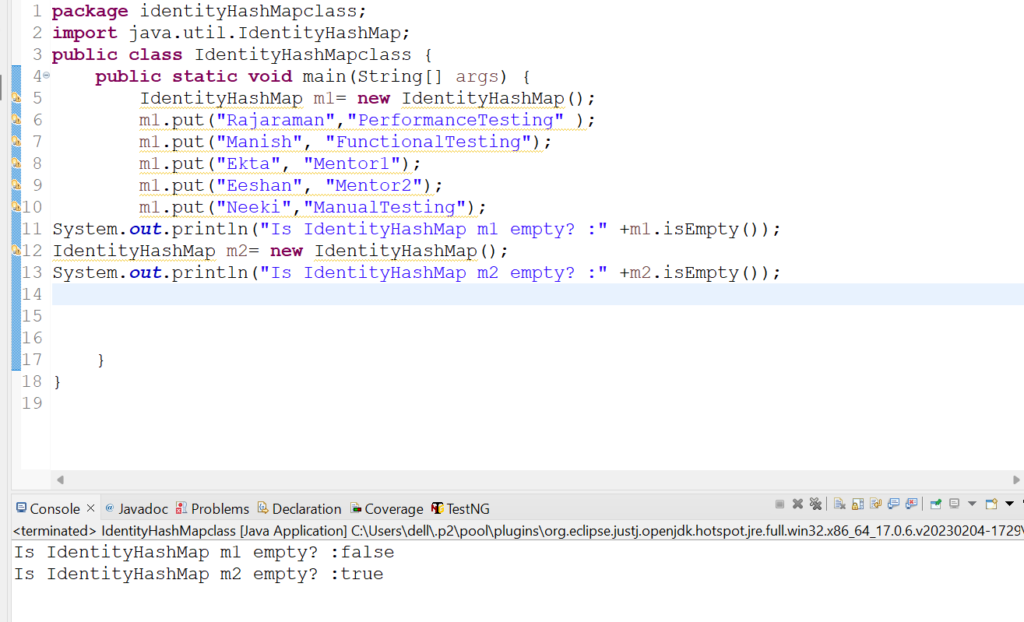
10. Let us check how keySet() method works in IdentityHashMap class.
Code Snippet:
package identityHashMapclass;
import java.util.IdentityHashMap;
public class IdentityHashMapclass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IdentityHashMap m1= new IdentityHashMap();
m1.put("Rajaraman","PerformanceTesting" );
m1.put("Manish", "FunctionalTesting");
m1.put("Ekta", "Mentor1");
m1.put("Eeshan", "Mentor2");
m1.put("Neeki","ManualTesting");
System.out.println(m1.keySet());
}
}
Output: [Manish, Eeshan, Ekta, Neeki, Rajaraman]
Screenshot:
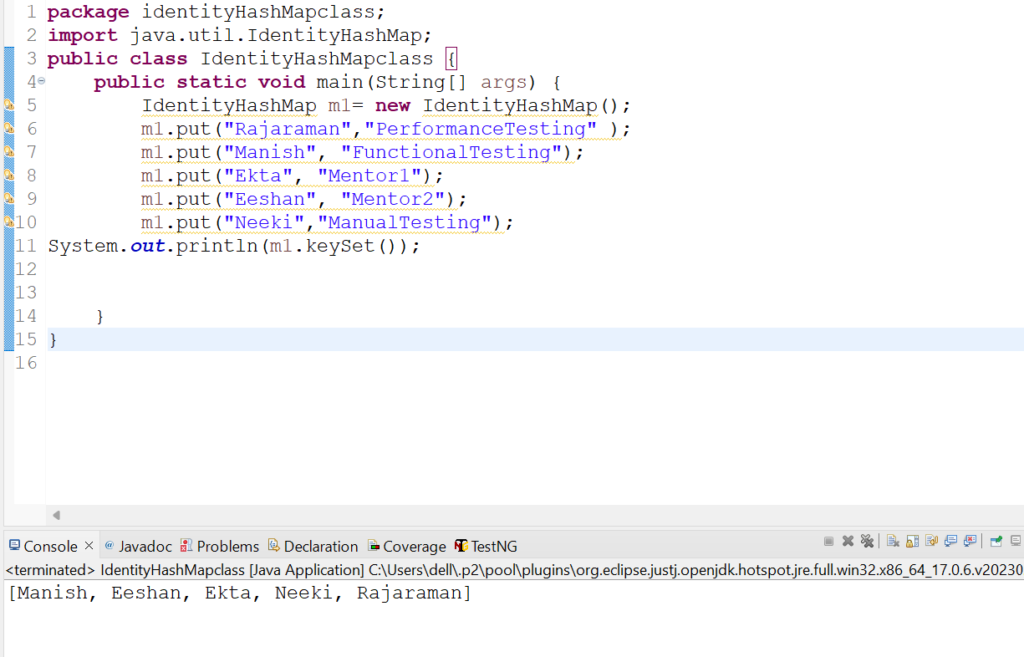
11. Let us check how remove(Object key) method works in IdentityHashMap class.
Code Snippet:
package identityHashMapclass;
import java.util.IdentityHashMap;
public class IdentityHashMapclass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IdentityHashMap m1= new IdentityHashMap();
m1.put("Rajaraman","Instructor2" );
m1.put("Manish", "Instructor1");
m1.put("Ekta", "Mentor1");
m1.put("Eeshan", "Mentor2");
m1.put("Neeki","Instructor3");
System.out.println(m1);
m1.remove("Rajaraman");
System.out.println("New key value pairs are:");
System.out.println(m1);
System.out.println(m1.remove("Deepesh"));
System.out.println(m1.remove("Manish"));
}
}
Output:
{Manish=Instructor1, Eeshan=Mentor2, Ekta=Mentor1, Neeki=Instructor3, Rajaraman=Instructor2}
New key value pairs are:
{Manish=Instructor1, Eeshan=Mentor2, Ekta=Mentor1, Neeki=Instructor3}
null
Instructor1
Screenshot:
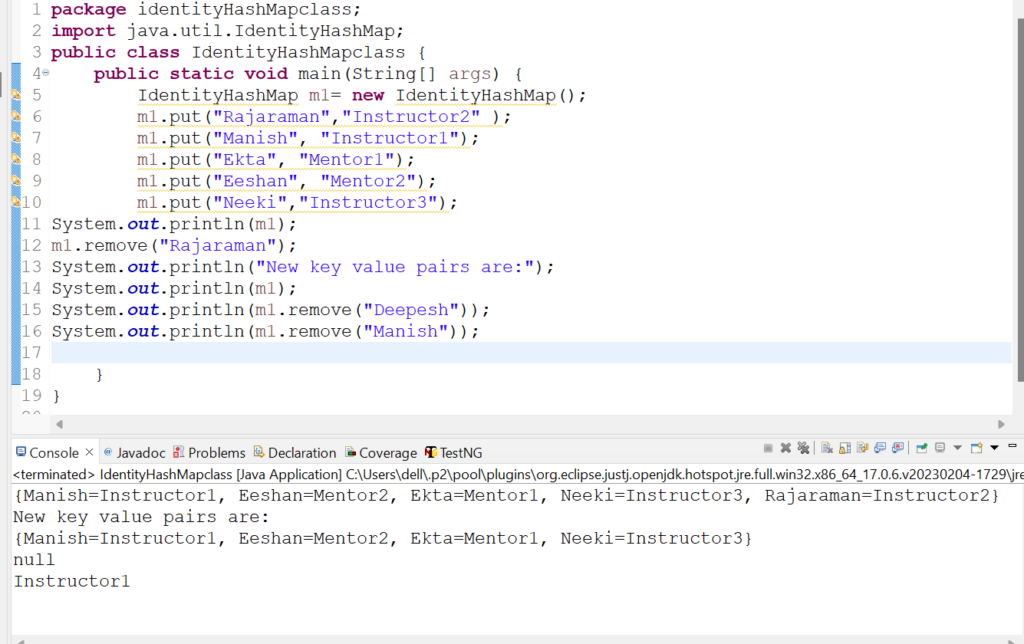
13. Let us check how putIfAbsent(Object key, Object value) method works in IdentityHashMap class.
Code Snippet:
package identityHashMapclass;
import java.util.IdentityHashMap;
public class IdentityHashMapClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IdentityHashMap m1= new IdentityHashMap();
m1.put("Rajaraman","Instructor2" );
m1.put("Manish", "Instructor1");
m1.put("Ekta", "Mentor1");
m1.put("Eeshan", "Mentor2");
m1.put("Neeki","Instructor3");
System.out.println(m1);
System.out.println(m1.putIfAbsent("Rajaraman", "Instructor2"));
System.out.println(m1);
System.out.println(m1.putIfAbsent("Deepesh","Instructor4"));
System.out.println(m1);
}
}
Output: {Manish=Instructor1, Eeshan=Mentor2, Ekta=Mentor1, Neeki=Instructor3, Rajaraman=Instructor2}
Instructor2
{Manish=Instructor1, Eeshan=Mentor2, Ekta=Mentor1, Neeki=Instructor3, Rajaraman=Instructor2}
null
{Deepesh=Instructor4, Manish=Instructor1, Eeshan=Mentor2, Ekta=Mentor1, Neeki=Instructor3, Rajaraman=Instructor2}
Screenshot:
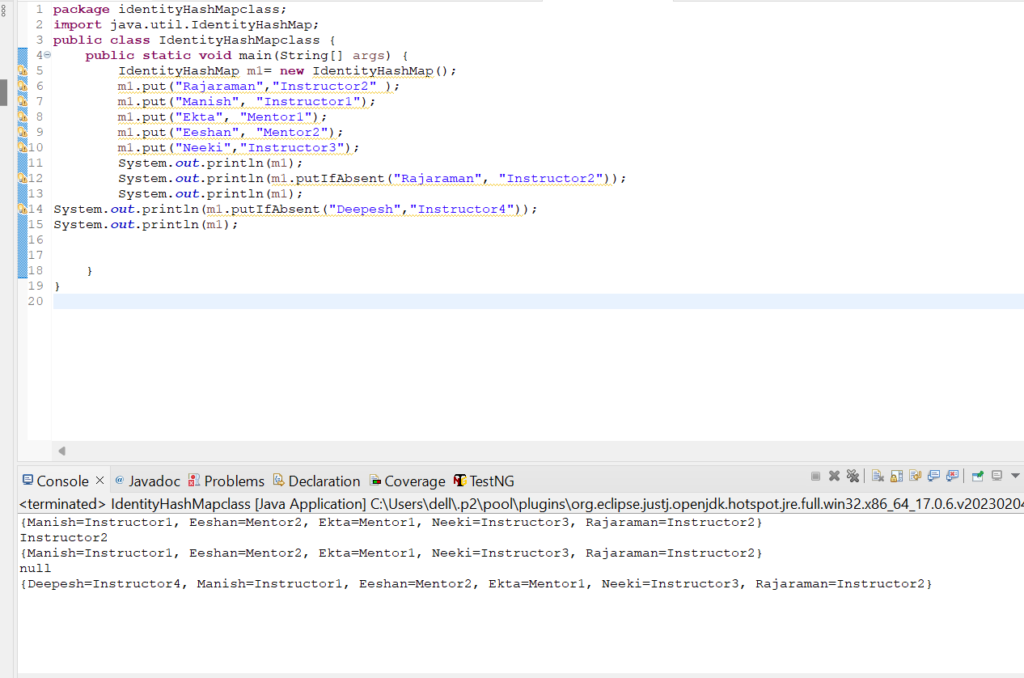
14. Let us check how replace(Object key, Object oldValue, Object newValue) method works in IdentityHashMap class.
Code Snippet:
package identityHashMapclass;
import java.util.IdentityHashMap;
public class IdentityHashMapClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IdentityHashMap m1= new IdentityHashMap();
m1.put("Rajaraman","Instructor2" );
m1.put("Manish", "Instructor1");
m1.put("Ekta", "Mentor1");
m1.put("Eeshan", "Mentor2");
m1.put("Neeki","Instructor3");
System.out.println(m1);
m1.replace("Rajaraman", "Instructor2", "SDET1");
System.out.println(m1);
}
}
Output: {Manish=Instructor1, Eeshan=Mentor2, Ekta=Mentor1, Neeki=Instructor3, Rajaraman=Instructor2}
{Manish=Instructor1, Eeshan=Mentor2, Ekta=Mentor1, Neeki=Instructor3, Rajaraman=SDET1}
Screenshot:
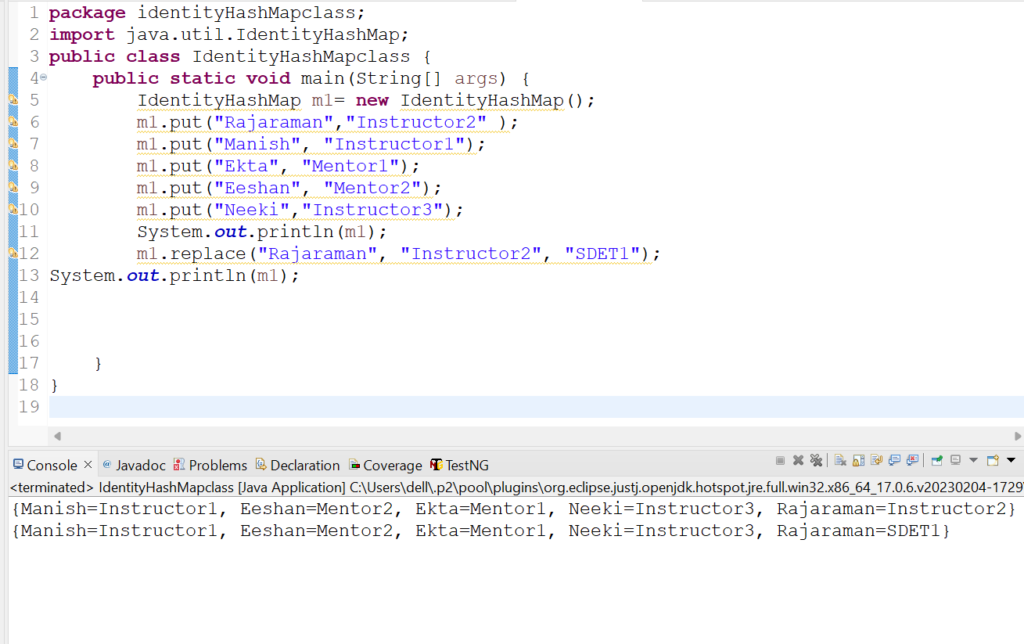
15. Let us check how replace(Object key, Object value) method works in IdentityHashMap class.
Code Snippet:
package identityHashMapclass;
import java.util.IdentityHashMap;
public class IdentityHashMapClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IdentityHashMap m1= new IdentityHashMap();
m1.put("Rajaraman","Instructor2" );
m1.put("Manish", "Instructor1");
m1.put("Ekta", "Mentor1");
m1.put("Eeshan", "Mentor2");
m1.put("Neeki","Instructor3");
System.out.println(m1);
m1.replace("Rajaraman", "SDET1");
System.out.println(m1);
}
}
Output:{Manish=Instructor1, Eeshan=Mentor2, Ekta=Mentor1, Neeki=Instructor3, Rajaraman=Instructor2}
{Manish=Instructor1, Eeshan=Mentor2, Ekta=Mentor1, Neeki=Instructor3, Rajaraman=SDET1}
Screenshot:
16. Let us check how entrySet() method works in IdentityHashMap class.
Code Snippet:
package identityHashMapclass;
import java.util.IdentityHashMap;
public class IdentityHashMapclass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IdentityHashMap m1= new IdentityHashMap();
m1.put("Rajaraman","Instructor2" );
m1.put("Manish", "Instructor1");
m1.put("Ekta", "Mentor1");
m1.put("Eeshan", "Mentor2");
m1.put("Neeki","Instructor3");
System.out.println(m1.entrySet());
}
}
Output: [Manish=Instructor1, Eeshan=Mentor2, Ekta=Mentor1, Neeki=Instructor3, Rajaraman=Instructor2]
Screenshot:
17. Let us check how iterator() method works in IdentityHashMap class.
Code Snippet:
package identityHashMapclass;
import java.util.IdentityHashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
public class IdentityHashMapclass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IdentityHashMap<String,String> m1= new IdentityHashMap<String,String>();
m1.put("Rajaraman","Instructor2" );
m1.put("Manish", "Instructor1");
m1.put("Ekta", "Mentor1");
m1.put("Eeshan", "Mentor2");
m1.put("Neeki","Instructor3");
Iterator<Entry<String, String>> itr= m1.entrySet().iterator();
while(itr.hasNext())
{
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
}
}
Output: Manish=Instructor1
Eeshan=Mentor2
Ekta=Mentor1
Neeki=Instructor3
Rajaraman=Instructor2
Screenshot:
18. Let us check how clone() method works in IdentityHashMap class.
Code Snippet:
package identityHashMapclass;
import java.util.IdentityHashMap;
public class IdentityHashMapclass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IdentityHashMap<String,String> m1= new IdentityHashMap<String,String>();
m1.put("Rajaraman","Instructor2" );
m1.put("Manish", "Instructor1");
m1.put("Ekta", "Mentor1");
m1.put("Eeshan", "Mentor2");
m1.put("Neeki","Instructor3");
System.out.println(m1);
System.out.println(m1.clone());
}
}
Output: {Manish=Instructor1, Eeshan=Mentor2, Ekta=Mentor1, Neeki=Instructor3, Rajaraman=Instructor2}
{Manish=Instructor1, Eeshan=Mentor2, Ekta=Mentor1, Neeki=Instructor3, Rajaraman=Instructor2}
Screenshot:
Difference between HashMap and IdentityHashMap
| SL NO: | HashMap | IdentityHashMap |
| 1 | Implements Map interface without violating map general contract. | Implements Map interface as well as violates map general contract |
| 2 | Uses object equality which is the equals() method for key and values comparision | Uses reference equality which is ‘==’ operator for key and values comparison. |
| 3 | While performing search operation it uses hashcode() method for hashing. | While performing search operation it uses System.IdentityHashCode() method for hashing. |
| 4 | For storing elements keys need to be immutable | For storing elements keys need not be immutable. |
| 5 | Performs poorer than IdentityHashMap | Performs better than HashMap |
Conclusion:
IdentityHashMap class is used for handling all the key and value pairsin an effective way. It is necessary to understand the usage of all the methods of IdentityHashMap class for better handling of IdentityHashMap elements. By thoroughly understanding the IdentityHashMap class and its methods developers and testers can utitlise those concepts in their real life tasks. Remember to practise, stay updated with the latest trends in Automation Software Testing Course,and maintain a positive attitude throughout your interview process.Automation testers can utlize all the methods of IdentityHashMap class to create better and effective test scripts for automation testing of web applications and websites.
Also, read my blogs on:
Consult Us