Stack class in Collection
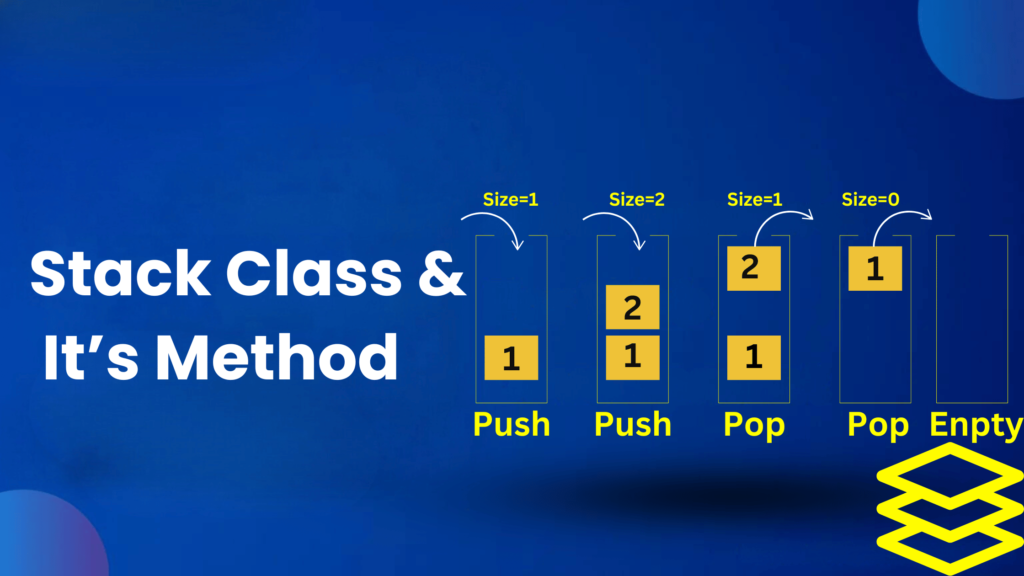
Stack Class and its methods
Before we start with Stack let us look at the following concepts
1.Legacy Classes
2.Collection Hierarchy
Legacy Classes
Legacy classes are those classes with the help of which we store various datas or Objects. These were present in JDK 1.0 version. The various legacy classes are Stack, Stack, HashTable,Properties,Dictionary.
Collection Hierarchy
The below diagram shows the Collection hierarchy consisting of classes and interfaces.

As per the scope of the blog our discussion will be limited to the Stack class
What is Stack class ?
Stack class is an implemented class of List interface,Collection interface and Iterable interface as well as sub class of Vector class which is used to store multiple elements. Stack class is a legacy class which was introduced in JDK 1.0. It comes from “java.utils” package. Stack class is an index based data structure and its underline data structure is growable or resizeable array. Duplicate elements can be stored in Stack class. Stack class allows any number of null values to be stored in it. Stack class follow the order of insertion. Stack class elements can be iterated by using Iterator and ListIterator methods as well as by Enumeration. Stack class is both thread safe and synchronized. It is slower due to synchronization. Its initial capacity is 10 and its threshold is when the current capacity is exceeded. Stack can double its size as it inherits Vector class’s growth strategy.
Methods of Stack class
| Method Name | Description |
| add(Object e) | This method is used to add a new element of any datatype into the Stack class. |
| addAll(Collection c) | This method is used to add all elements of different datatypes into the Stack class. |
| clear() | It is used to clear all the elements from the Set interface but it does not clear the Stack class. |
| contains(Object o) | This method is used to check the presence of a Collection element in the Stack class. It returns ‘true’ value if the element is present in Stack class and ‘false’ value if the element is not present in the Stack class. |
| containsAll(Collection c) | This method is used to check if the Stack class contains all the collection elements. It returns ‘true’ value if all the elements are present in Stack class and ‘false’ value if any one of the element is not present in the Stack class. |
| isEmpty() | This method checks if the given Stack class is empty |
| iterator() | This method is used to iterate sequentially all the Collection elements present in a Stack class. |
| remove(Object o) | This method is used to remove a specified collection element from the Stack class. |
| removeAll(Collection c) | This method removes all those Collection elements from the current Stack class which are present in another Stack class. |
| retainAll(Collection c) | This method retains all those elements from the current Stack class which are present in another Stack class and removes those elements which are present in current Stack class but not in another Stack class and vice versa. |
| size() | This method is used to find out and display the number of Collection elements present in the Stack class. |
| toArray() | This method is used to convert all collection elements present in Stack class into an array. |
| toString() | This method is used to convert all collection elements present in Stack class into a String. |
| equals() | This method is used to check if two Stack classes are equal. It returns ‘true’ value if elements as well as size of elements present in one Stack class is equal to the elements and its size present in another Stack class. If the elements and the size of elements present in one Vectro class is not equal to the elements and its size present in another Stack class then it returns ‘false’ value. |
| clone() | This method is used to create a shallow copy of the elements present in the Stack class. |
| addElement(Object obj) | It is used to add an element at the end of the Stack |
| firstElement() | It is used to display the first element of the Stack class. |
| lastElement() | It is used to display the last element of the Stack class. |
| removeElement(Object obj) | It is used to remove a particular element from Stack class. |
| removeAllElements() | It is used to remove all the elements from Stack class. |
| removeElementAt(int index) | It is used to remove a Stack element present at a particular index position. |
| get(int index) | It is used to display an element of Stack class present at a particular index. |
| set(int index,Object element) | It is used to replace a Stack class element present at a particular index position with another element. |
| capacity() | It is used to display the current capacity of the Stack or length of the array present in the Vectoe class. |
| elements() | It is used to display the enumeration of elements present in the Stack class. |
| listIterator() | This method is used to iterate sequentially in forward as well as backward direction all the Collection elements present in the Stack class. |
| indexOf(Object o) | It is used to display the index of first occurrence of Stack class element.It gives-1 if the specified element is not present in Stack class. |
| peek() | This method is used to fetch or point out the topmost element of the ArrayDeque which is displayed in output console but does not remove that element from the ArrayDeque class. |
| pop() | It is used to remove the last element from Stack Class. |
| push(Object item) | It is used to add an element at the end of the Stack |
| search(Object o) | It is used to search a particular element from the list of elements present in Stack Class. The position of element starts from “1” and the last element of Stack will have position “1”.If there are similar elements present in Stack then the position of that element closer to last element will be considered. If the element to be searched is not present in Stack then its position is mentioned as “-1”. |
1. Let us check the usage of add(Object e) method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
System.out.println(a1);
}
}
Output: [Hi, Hey, 16, 16, 20, 23, 34]
Screenshot:

2. Let us check the usage of addAll(Collection c) method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
Stack a2= new Stack();
a2.addAll(a1);
System.out.println(a2);
}
}
Output: [Hi, Hey, 16, 16, 20, 23, 34]
Screenshot:

3. Let us check the usage of clear() method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
a1.clear();
System.out.println(a1);
}
}
Output: []
Screenshot:

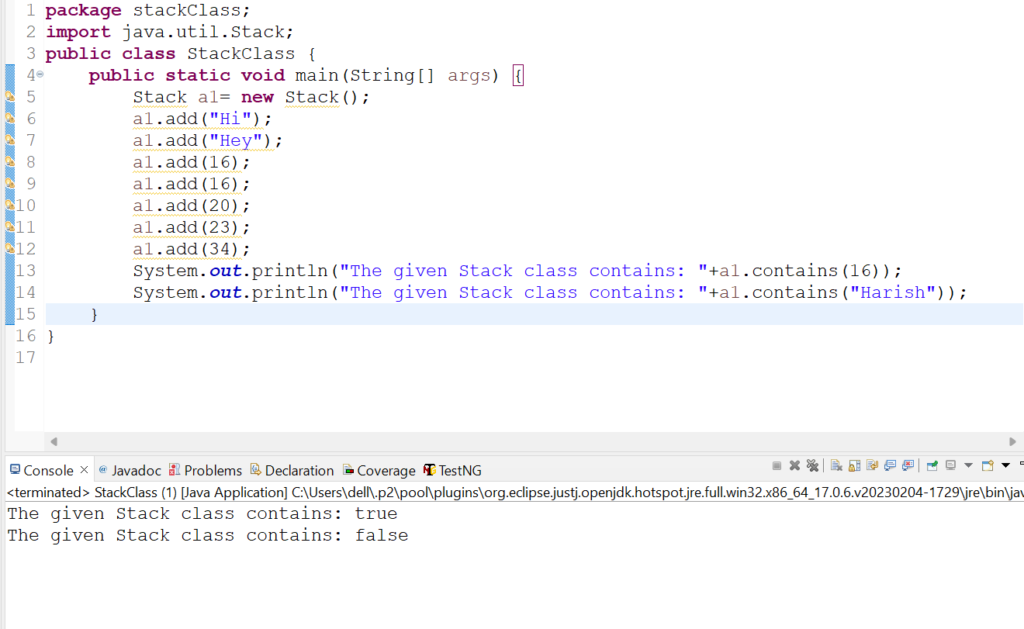
4.Let us check the usage of contains(Object o) method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
System.out.println("The given Stack class contains: "+a1.contains(16));
System.out.println("The given Stack class contains: "+a1.contains("Harish"));
}
}
Output: The given Stack class contains: true
The given Stack class contains: false
Screenshot:
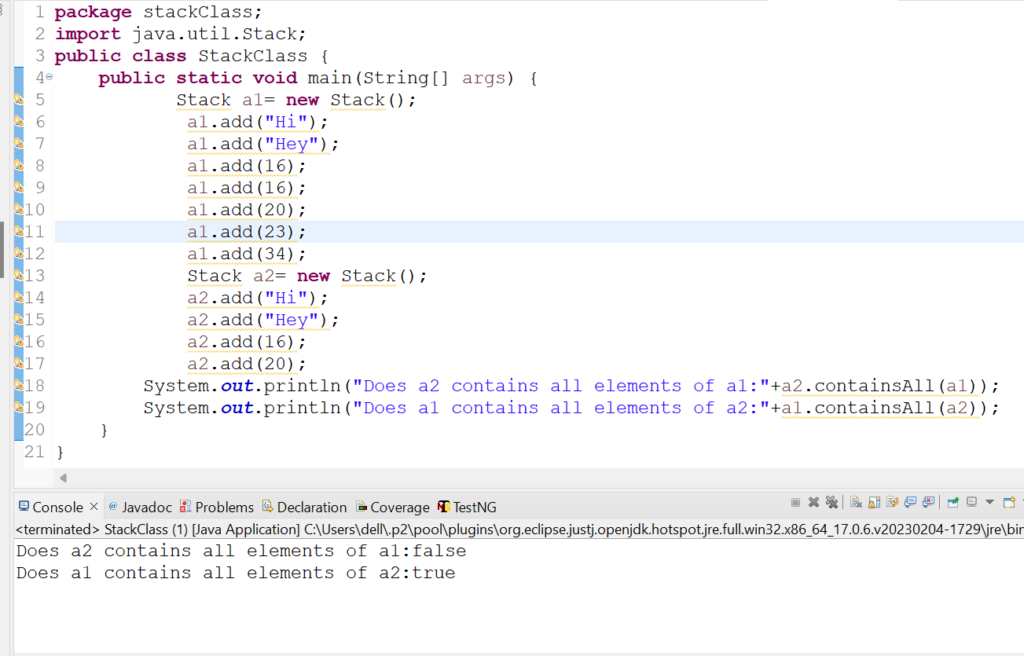
5.Let us check the usage of containsAll(Collection c) method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
Stack a2= new Stack();
a2.add("Hi");
a2.add("Hey");
a2.add(16);
a2.add(20);
System.out.println("Does a2 contains all elements of a1:"+a2.containsAll(a1));
System.out.println("Does a1 contains all elements of a2:"+a1.containsAll(a2));
}
}
Output:
Does a2 contains all elements of a1:false
Does a1 contains all elements of a2:true
Screenshot:
6. Let us check the usage of isEmpty() method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
Stack a2= new Stack();
System.out.println("Is a1 Stack class empty?: "+a1.isEmpty());
System.out.println("Is a2 Stack class empty?: "+a2.isEmpty());
}
}
Output:
Is a1 Stack class empty?: false
Is a2 Stack class empty?: true
Screenshot:

7. Let us check the usage of iterator() method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
Iterator a2= a1.iterator();
System.out.println("The collection elements values are: ");
while(a2.hasNext())
{
System.out.println(a2.next());
}
}
}
Output:
The collection elements values are:
Hi
Hey
16
16
20
23
34
Screenshot:

8. Let us check the usage of remove(Object o) method in Stack class.
Case 1: For removing an element containing words:
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
a1.remove("Hey");
a1.remove("Hi");
System.out.println(a1);
}
}
Output: [16, 16, 20, 23, 34]
Screenshot:

Case 2: For removing an element containing numeric value:
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
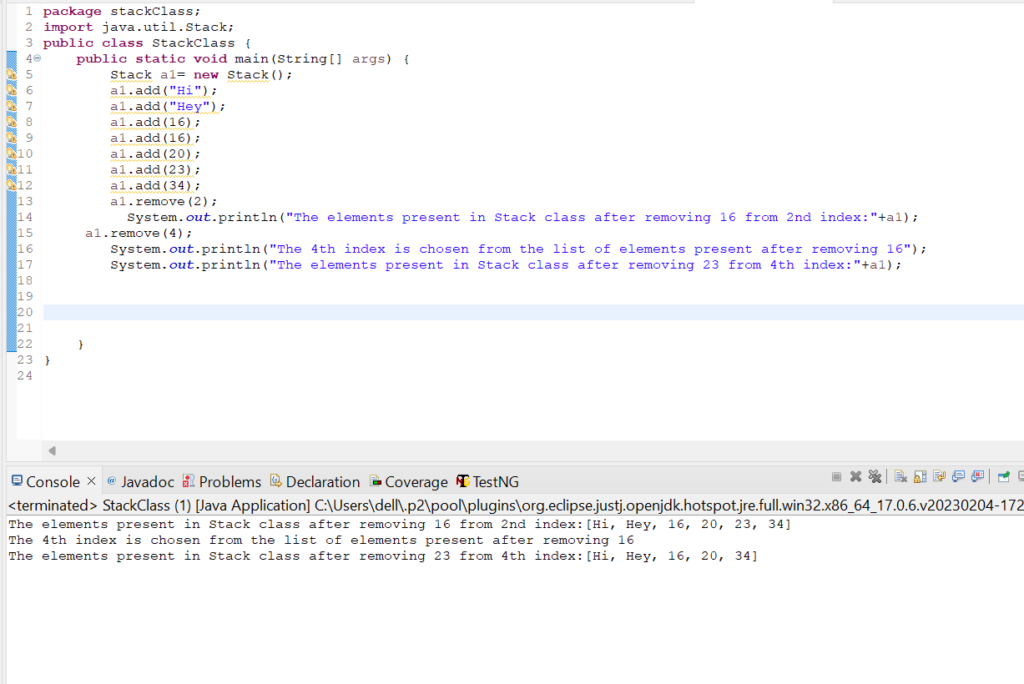
a1.remove(2);
System.out.println("The elements present in Stack class after removing 16 from 2nd index:"+a1);
a1.remove(4);
System.out.println("The 4th index is chosen from the list of elements present after removing 16");
System.out.println("The elements present in Stack class after removing 23 from 4th index:"+a1);
}
}
Output: The elements present in Stack class after removing 16 from 2nd index:[Hi, Hey, 16, 20, 23, 34]
The 4th index is chosen from the list of elements present after removing 16
The elements present in Stack class after removing 23 from 4th index:[Hi, Hey, 16, 20, 34]
Screenshot:
9. Let us check the usage of removeAll(Collection c) method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
Stack a2= new Stack();
a2.add("Hi");
a2.add("Hey");
a2.add(16);
a2.add(20);
a1.removeAll(a2);
System.out.println("Elements present in a1 after removing a2 elements from a1 are:"+a1);
}
}
Output:
Elements present in a1 after removing a2 elements from a1 are:[23, 34]
Screenshot:

10. Let us check the usage of retainAll(Collection c) method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
Stack a2= new Stack();
a2.add("Hi");
a2.add("Hey");
a2.add(16);
a2.add(20);
a1.retainAll(a2);
System.out.println("Elements present in a1 after retaining a2 elements are:"+a1);
}
}
Output: Elements present in a1 after retaining a2 elements are:[Hi, Hey, 16, 16, 20]
Screenshot:

11. Let us check the usage of size() method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
System.out.println("The size of the collection elements present in the Stack class is: "+a1.size());
}
}
Output: The size of the collection elements present in the Stack class is: 7
Screenshot:

12. Let us check the usage of toArray() method in Stack class
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
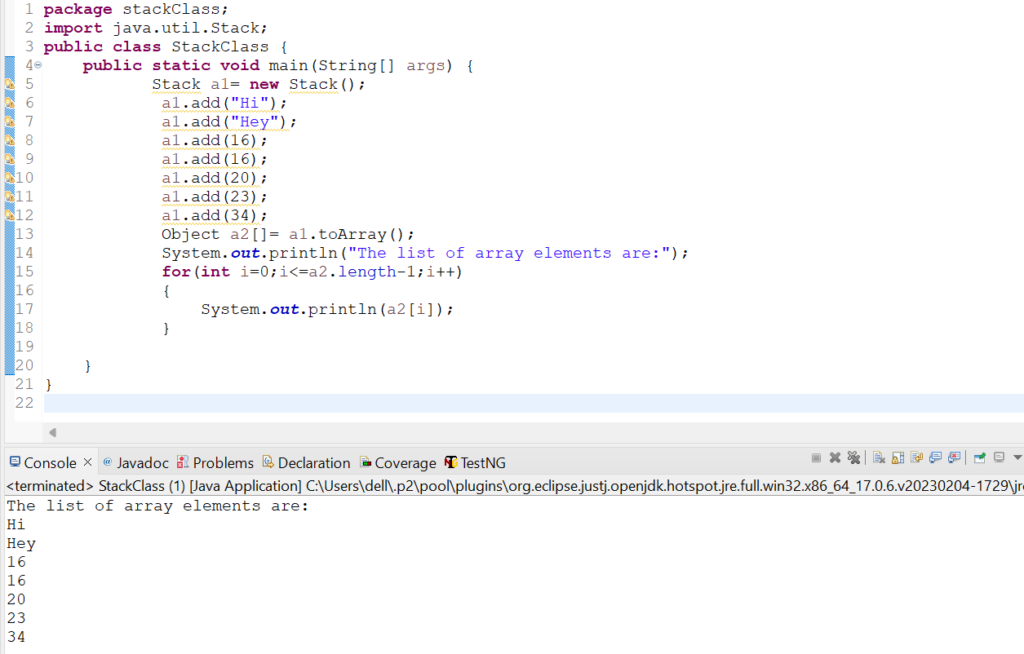
Object a2[]= a1.toArray();
System.out.println("The list of array elements are:");
for(int i=0;i<=a2.length-1;i++)
{
System.out.println(a2[i]);
}
}
}
Output: The list of array elements are:
Hi
Hey
16
16
20
23
34
Screenshot:

13. Let us check the usage of toString() method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
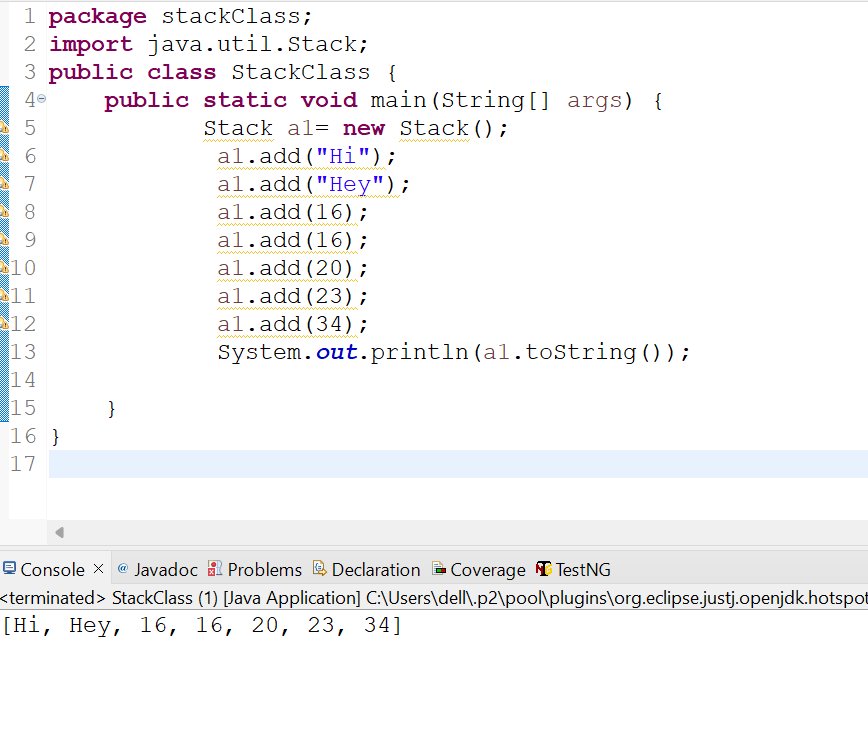
System.out.println(a1.toString());
}
}
Output: [Hi, Hey, 16, 20, 23, 34]
Screenshot:

14. Let us check the usage of equals() method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
Stack a2= new Stack();
a2.add("Hi");
a2.add("Hey");
a2.add(16);
a2.add(16);
a2.add(20);
a2.add(23);
a2.add(34);
Stack a3= new Stack();
a3.add("Hi");
a3.add("Hey");
a3.add(16);
a3.add(20);
System.out.println("Is Stack class a1 equal to a2 ?:"+ a1.equals(a2));
System.out.println("Is Stack class a2 equal to a3 ?:"+ a2.equals(a3));
}
}
Output: Is Stack class a1 equal to a2 ?:true
Is Stack class a2 equal to a3 ?:false
Screenshot:
15. Let us check the usage of clone() method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
System.out.println("List of elements in Stack class: "+a1);
Stack clonea1= new Stack();
clonea1=(Stack)a1.clone();
System.out.println("List of elements after using clone method:"+ clonea1);
}
}
Output: List of elements in Stack class: [Hi, Hey, 16, 16, 20, 23, 34]
List of elements after using clone method:[Hi, Hey, 16, 16, 20, 23, 34]
Screenshot:
16. Let us check the usage of addElement(Object obj) method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
a1.addElement(343);
System.out.println(a1);
}
}
Output: [Hi, Hey, 16, 16, 20, 23, 34, 343]
Screenshot:

17. Let us check the usage of firstElement() method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
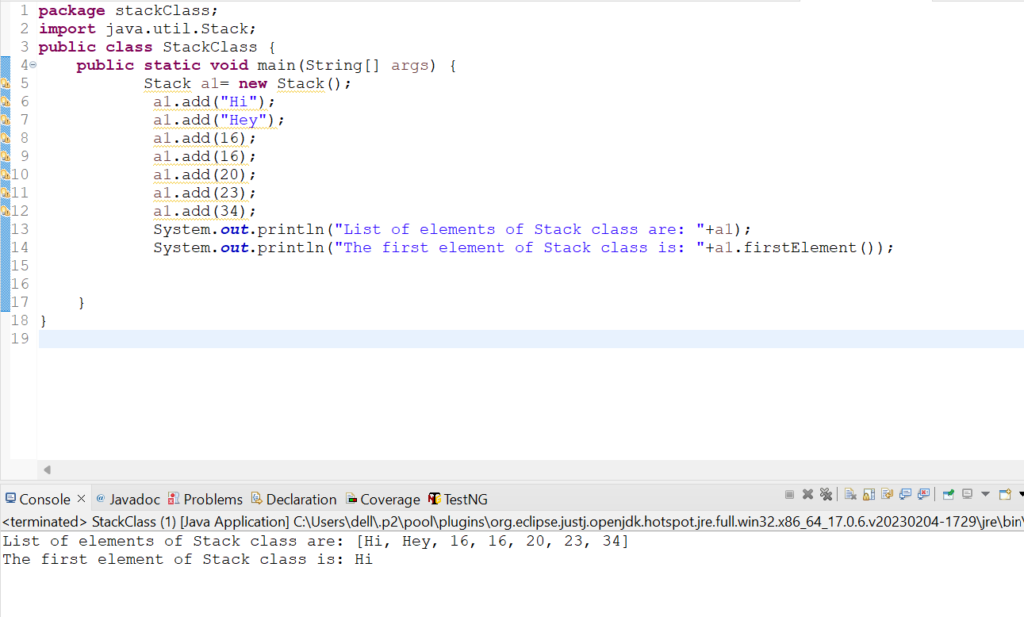
System.out.println("List of elements of Stack class are: "+a1);
System.out.println("The first element of Stack class is: "+a1.firstElement());
}
}
Output: List of elements of Stack class are: [Hi, Hey, 16, 16, 20, 23, 34]
The first element of Stack class is: Hi
Screenshot:

18. Let us check the usage of lastElement() method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
System.out.println("List of elements of Stack class are: "+a1);
System.out.println("The last element of Stack class is: "+a1.lastElement());
}
}
Output: List of elements of Stack class are: [Hi, Hey, 16, 16, 20, 23, 34]
The last element of Stack class is: 34
Screenshot:
19. Let us check the usage of removeElement(Object obj) method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
System.out.println("List of elements of Stack class are: "+a1);
a1.removeElement(16);
System.out.println("Elements present after removing 16 are :" +a1);
}
}
Output: List of elements of Stack class are: [Hi, Hey, 16, 16, 20, 23, 34]
Elements present after removing 16 are :[Hi, Hey, 16, 20, 23, 34]
Screenshot:

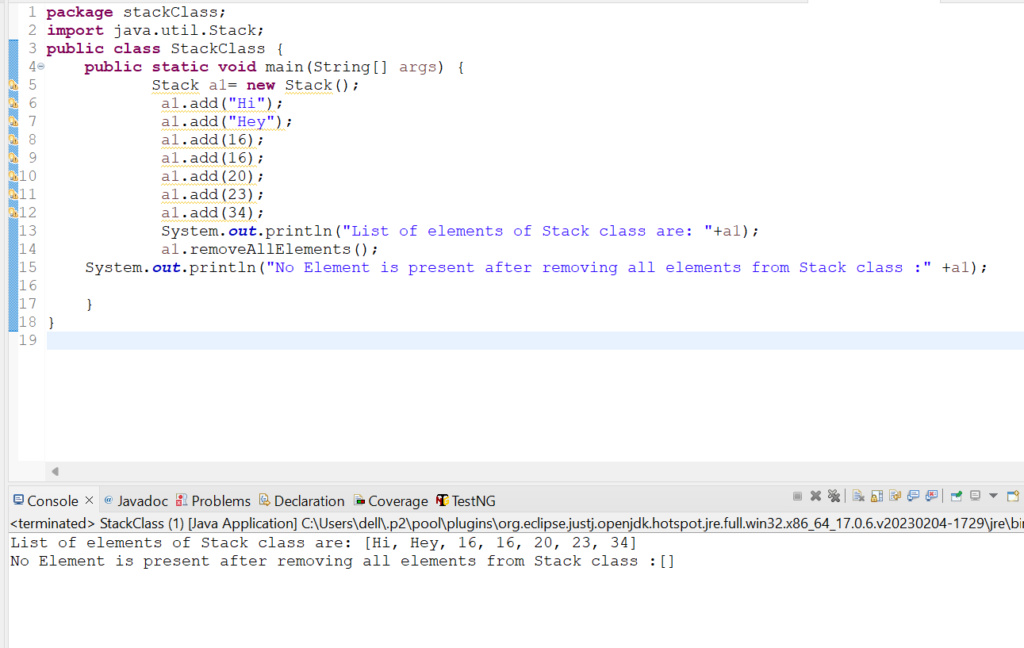
20. Let us check the usage of removeAllElements() method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
System.out.println("List of elements of Stack class are: "+a1);
a1.removeAllElements();
System.out.println("No Element is present after removing all elements from Stack class :" +a1);
}
}
Output: List of elements of Stack class are: [Hi, Hey, 16, 16, 20, 23, 34]
No Element is present after removing all elements from Stack class :[]
Screenshot:

21. Let us check the usage of removelElementAt(int index) method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
System.out.println("List of elements of Stack class are: "+a1);
a1.removeElementAt(3);
System.out.println("Elements present after removing element present at index 3 are:" +a1);
}
}
Output: List of elements of Stack class are: [Hi, Hey, 16, 16, 20, 23, 34]
Elements present after removing element present at index 3 are:[Hi, Hey, 16, 20, 23, 34]
Screenshot:

22. Let us check the usage of get(int index) method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
System.out.println("List of elements in Stack class are: "+a1);
System.out.println("The element present in index position 2 is: "+a1.get(2));
}
}
Output: List of elements in Stack class are: [Hi, Hey, 16, 16, 20, 23, 34]
The element present in index position 2 is: 16
Screenshot:
23. Let us check the usage of set(int index,Object element) method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
System.out.println("List of elements in Stack class are: "+a1);
System.out.println("The element to be replaced is: "+a1.set(2,56));
System.out.println("New List of elements after replacement are :" +a1);
}
}
Output: List of elements in Stack class are: [Hi, Hey, 16, 16, 20, 23, 34]
The element to be replaced is: 16
New List of elements after replacement are :[Hi, Hey, 56, 16, 20, 23, 34]
Screenshot:

24. Let us check the usage of capacity() method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
System.out.println("The current capacity of this Stack class is: "+ a1.capacity());
}
}
Output: The current capacity of this Stack class is: 10
Screenshot:

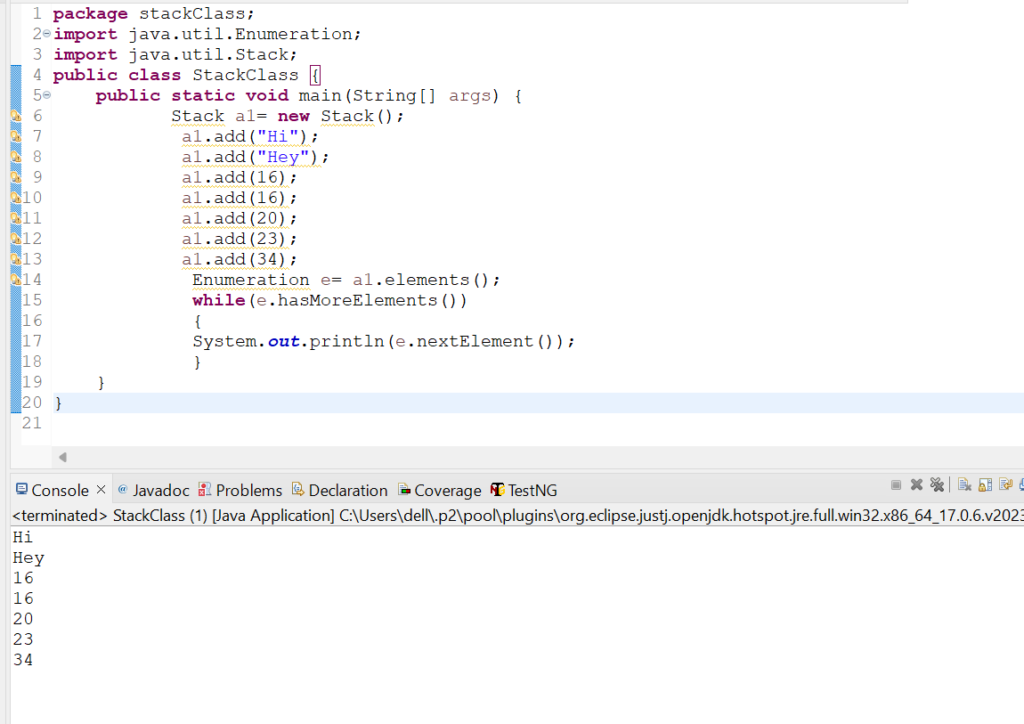
25. Let us check the usage of elements() method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
Enumeration e= a1.elements();
while(e.hasMoreElements())
{
System.out.println(e.nextElement());
}
}
}
Output: Hi
Hey
16
16
20
23
34
Screenshot:
26. Let us check the usage of listIterator() method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.ListIterator;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
ListIterator a2= a1.listIterator();
while(a2.hasNext()==true)
{
System.out.println("Next method "+a2.next());
}
while(a2.hasPrevious()==true)
{
System.out.println("Previous Method "+a2.previous());
}
}
}
Output: Next method Hi
Next method Hey
Next method 16
Next method 16
Next method 20
Next method 23
Next method 34
Previous Method 34
Previous Method 23
Previous Method 20
Previous Method 16
Previous Method 16
Previous Method Hey
Previous Method Hi
Screenshot:

27. Let us check the usage of indexOf(Object o) method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
System.out.println("Index of 16 is :"+a1.indexOf(16));
System.out.println("Index of 45 is :"+a1.indexOf(45));
}
}
Output: Index of 16 is :2
Index of 45 is :-1
Screenshot:

28. Let us check the usage of peek() method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
System.out.println("Initial List of Stack elements: "+a1);
System.out.println("Element on which peek method is applied: "+a1.peek());
System.out.println("New List of Stack elements after using peek method: "+a1);
}
}
Output:
Initial List of Stack elements: [Hi, Hey, 16, 16, 20, 23, 34]
Element on which peek method is applied: 34
New List of Stack elements after using peek method: [Hi, Hey, 16, 16, 20, 23, 34]
Screenshot:

29. Let us check the usage of pop() method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
System.out.println("List of elements present in Stack Class:"+a1);
System.out.println("Element which is removed "+ a1.pop());
System.out.println("List of elements present after removal:"+a1);
}
}
Output: List of elements present in Stack Class:[Hi, Hey, 16, 16, 20, 23, 34]
Element which is removed 34
List of elements present after removal:[Hi, Hey, 16, 16, 20, 23]
Screenshot:

30. Let us check the usage of push(Object item) method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(23);
a1.add(34);
a1.push(343);
System.out.println(a1);
}
}
Output: [Hi, Hey, 16, 16, 20, 23, 34, 343]
Screenshot:

31. Let us check the usage of search(Object o) method in Stack class.
Code Snippet:
package stackClass;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack a1= new Stack();
a1.add("Hi");
a1.add("Hey");
a1.add(16);
a1.add(16);
a1.add(20);
a1.add(34);
a1.add(34);
System.out.println(a1.search(343));
System.out.println(a1.search(34));
}
}
Output: -1
1
Screenshot:

Difference between ArrayList and Stack
| SL NO: | ArrayList | Stack |
| 1 | It is not a Legacy class | It is a Legacy class |
| 2 | Neither thread safe nor synchronized | Both thread safe and synchronized |
| 3 | Faster due to no synchronization | Slower due to synchronization |
| 4 | Size increases by 50% | Size gets doubled. |
| 5 | Belongs to Collection framework | Belongs to original version of Java(1.0) |
| 6 | Iterator,ListIterator are used. | Enumeration,Iterator and ListIterator are used. |
Conclusion
Stack class is used for handling all the Collection elements in an effective way. It is necessary to understand the usage of all the methods of Stack class for better handling of Collection elements. Remember to practise, stay updated with the latest trends in Automation Software Testing Course,and maintain a positive attitude throughout your interview process.By thoroughly understanding the Stack class and its methods developers and testers can utitlise those concepts in their real life tasks.
Also, read my blogs on:
Consult Us