Top 18 java collection interview questions (2024)
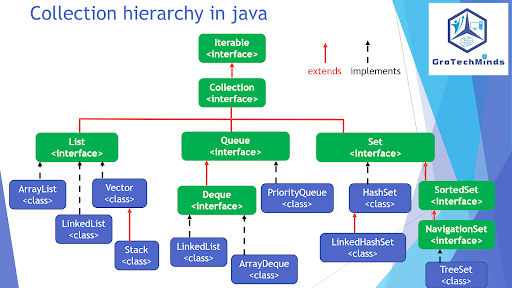
1. Differentiate between Collection and collections in the context of Java.
| Collection | Collections |
| 1. It is an interface. The interface can also contain abstract and default methods. | 1. It is a class |
| 2. It extends the iterable interface. | 2. It extends the Object class. |
| 3. Collection has got many interface and classes in it. | 3. It has lot of methods that can be used to work on the collection. |
| 4. It doesn’t have any direct implementation as it is an interface. But you can implement the collection interface by using various Java classes, like ArrayList, HashSet, and PriorityQueue. | 4. As it is a final class, meaning it can not be subclassed. It doesn’t have any public constructors, so its methods are accessed statically. |
| ArrayList | LinkedList |
| 1. ArrayList acts as List | 1. LinkedList acts as List & Deque. |
| 2. The underlying data-structure of ArrayList is a growable and resizable array. | 2. The Underlying data-structure of LinkedList is “Doubly LinkedList” OR “Circular LinkedList”. |
| 3. Memory efficient. It only stores the object in the list. | 3. Memory is inefficient. It stores the object and the pointers to next and previous nodes. |
| 4. ArrayList are good for retrieval operations. | 4. LinkedList are good for insertion or deletion operations. |
| 5. ArrayList are worst for insertion or deletion operations. | 5. LinkedList is the worst for retrieval operations. |
| Feature | ArrayList | Vector |
| Synchronization | Not synchronized | Synchronized |
| Thread Safe? | Not thread-safe | Thread-safe |
| Performance | Faster due to no synchronization | Slower due to synchronization overhead |
| Growth Factor | Increases its size by 50% | Doubles its size |
| Legacy | Part of collection framework | Part of the original version of Java (1.0) |
| Enumeration | Uses Iterator | Uses Enumeration and Iterator |
| List | Set |
| 1. List is an Index based data Structure. | 1. Set is not an index based data Structure. It stores the data according to hashcode values. |
| 2. List Can Store Duplicate Elements. | 2. Set does not allow storing duplicate elements. |
| 3. List can store any number of null values. | 3. Set can store only one null value in it. |
| 4. List follows the insertion order. | 4. Set does not follow the insertion order. |
| 5. We can iterate (get) the list element by Iterator and ListIterator. | 5. We can Iterate the set elements by Iterator only. |
| 6. ArrayList, LinkedList, Vector and Stack are implemented classes of List. | 6. HashSet, LinkedHashSet, TreeSet are implemented classes of Set. |
| Iterator | ListIterator |
| 1. We can get an Iterator cursor by iterator() method. Iterator itr=l.iterator(); | 1. We can get ListIterator cursor by listIterator() method. ListIterator litr=l.listIterator(); |
| 2. Iterator cursor can be used with any Collection object. | 2. ListIterator cursor can be used with only List implemented classes. i.e. ArrayList, LinkedList, Vector & Stack. |
| 3. Iterator Methods are: hasNext(), next(), remove(). | 3. ListIterator Methods are: hasNext(), next(), hasPrevious(), previous(), remove(), set(). |
| 4. By using the Iterator cursor, We can retrieve the elements only in forward direction. | 4. By using ListIterator cursor, We can retrieve the elements in forward & backward direction. |
| 5. By using the Iterator cursor, We can read & remove the elements. | 5.By using ListIterator cursor, We can read, remove, replace & add the elements. |
| Feature | Array | ArrayList |
| Size | Fixed size | Dynamic size |
| Type | Can hold primitives and objects | Can hold only objects |
| Syntax | int[] arr = new int[10]; | ArrayList list = new ArrayList(); |
| Memory Allocation | Allocated at compile-time | Allocated at runtime |
| Type Safety | Type safe | Type safe with generics |
| Iterator | No built-in iterator | Supports Iterator and ListIterator |
| Usage | Used when the size of the array is known and fixed | Used when the size is dynamic and can change |
We can add null elements in a HashSet but we cannot add null elements in a TreeSet.
| Collection Type | Class | Thread Safe | Synchronized |
| List | |||
| ArrayList | No | No | |
| Vector | Yes | Yes | |
| LinkedList | No | No | |
| Stack | Yes | Yes | |
| Set | |||
| HashSet | No | No | |
| LinkedHashSet | No | No | |
| TreeSet | No | No | |
| Map | |||
| HashMap | No | No | |
| Hashtable | Yes | Yes | |
| LinkedHashMap | No | No | |
| TreeMap | No | No | |
| Dictionary | Yes | Yes | |
| WeakHashMap | No | No | |
| IdentityHashMap | No | No | |
| Properties | Yes | Yes | |
| Queue | |||
| LinkedList | No | No | |
| PriorityQueue | No | No | |
| ArrayDeque | No | No |
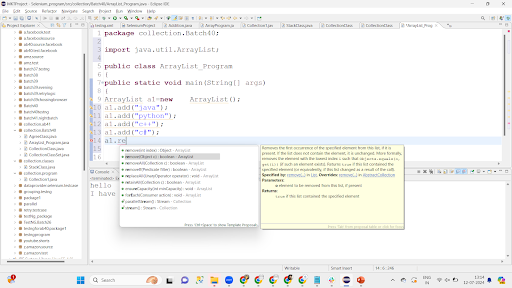
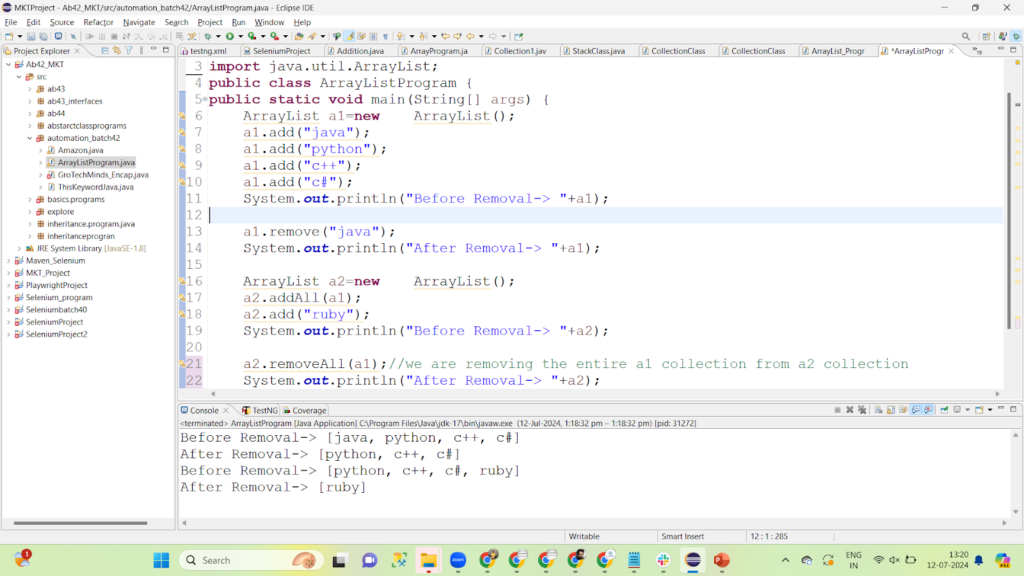
Remove(Object)->It Removes the particular object from the Collection.
RemoveAll(Collection)->It removes the entire collection from the given Collection.
Remove Method:
Remove All Method:
Code Snippet:
package automation_batch42;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArrayListProgram {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList a1=new ArrayList();
a1.add("java");
a1.add("python");
a1.add("c++");
a1.add("c#");
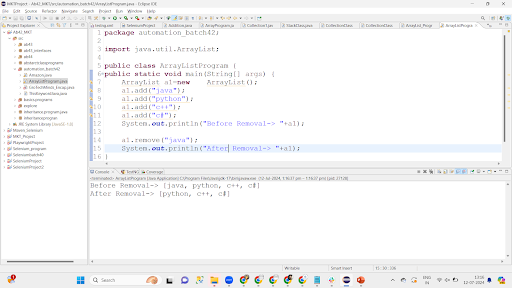
System.out.println("Before Removal-> "+a1);
a1.remove("java");
System.out.println("After Removal-> "+a1);
ArrayList a2=new ArrayList();
a2.addAll(a1);
a2.add("ruby");
System.out.println("Before Removal-> "+a2);
a2.removeAll(a1);//we are removing the entire a1 collection from a2 collection
System.out.println("After Removal-> "+a2);
}
}
13. Demonstrate ArrayList Class Methods.
Some of the ArrayList Methods are:
add(E e)
addAll(Collection c)
contains(Object o)
containsAll(Collection c)
isEmpty()
remove(Object o)
removeAll(Collection c)
size()
clear()
Code Snippet:
public class ArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList al=new ArrayList();
al.add(100);
al.add(200);
al.add(300);
System.out.println(al); // output will be [100, 200, 300]
}
}

Code Snippet:
public class ArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{ ArrayList al=new ArrayList();
al.add(100);
al.add(200);
System.out.println(al); // output:- [100, 200]
ArrayList al2=new ArrayList();
al2.add("aa");
al2.add("bb");
System.out.println(al2); // output:- [aa, bb]
al.addAll(al2);
System.out.println(al); // output:- [100, 200, aa, bb]
}
}

Code Snippet:
public class ArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList al=new ArrayList();
al.add("aa");
al.add("bb");
System.out.println(al); // Output: [aa, bb]
al.clear();
System.out.println("After Clearing the data "+al); // Output: []
}
}

Code Snippet:
public class ArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList al=new ArrayList();
al.add("aa");
al.add("bb");
System.out.println(al.contains("aa")); // Output: true
}
}

Code Snippet:
public class ArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList al=new ArrayList();
al.add("aa");
al.add("bb");
ArrayList al2=new ArrayList();
al2.add("aa");
al2.add("bb");
System.out.println(al.containsAll(al2)); //Output: true
}

Code Snippet:
public class ArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList al=new ArrayList();
al.add("aa");
al.add("bb");
System.out.println(al.isEmpty()); // Output: false
}
}

Code Snippet:
public class ArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList al=new ArrayList();
al.add("aa");
al.add("bb");
System.out.println(al); //output: [aa, bb]
al.remove("aa");
System.out.println(al); // Output: [bb]
}
}

Code Snippet:
public class ArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList al=new ArrayList();
al.add("aa");
al.add("bb");
System.out.println(al); // Output: [aa, bb]
ArrayList al2=new ArrayList();
al2.add("aa");
al2.add("cc");
al.removeAll(al2);
System.out.println(al); // Output: [bb]
}
}

Code Snippet:
public class ArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList al=new ArrayList();
al.add("aa");
al.add("bb");
System.out.println(al.size()); // Output: 2
}
}

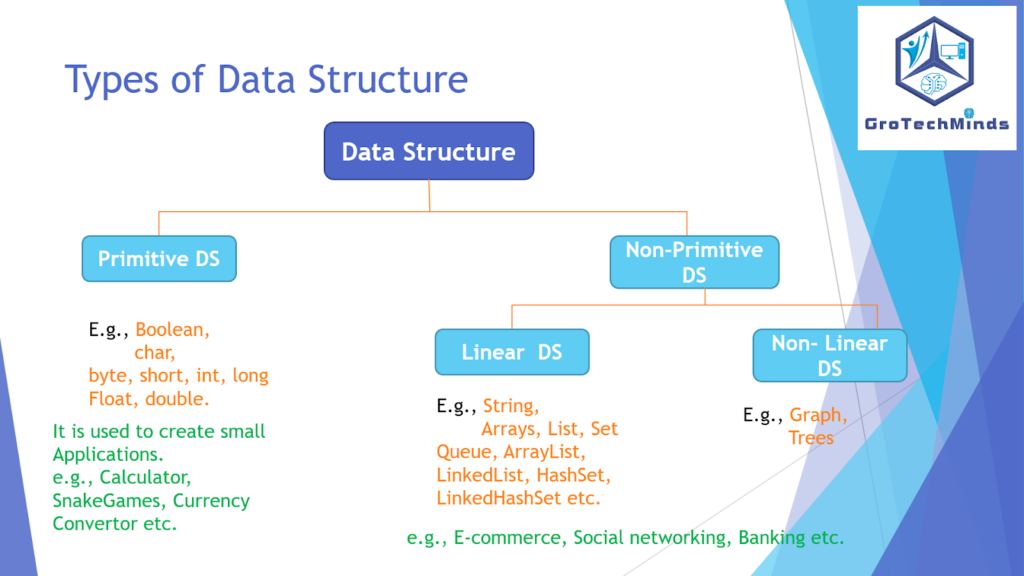
14. Types of Data Structure in Java.
15. What are cursors in Java?
A Java Cursor is an Iterator, which is used to iterate or traverse or retrieve a Collection or Stream object’s elements one by one. There are three cursors in Java.
1) Iterator 2) ListIterator & 3) Enumeration.
- Enumeration is the cursor which is used to retrieve Collection objects one by one.
- Enumeration was introduced in JDK 1.0 version.
- Enumeration cursor can be used only with Legacy Classes. i.e. Vector & Stack.
- Enumeration Cursor can be get by elements() method.
Enumeration e = v.elements();
- Methods of Enumeration cursor are:-
hasMoreElements(), nextElement()
- Enumeration cursor can be used to retrieve the elements only in forward direction.
- Enumeration cursor can be used only for read operations.
Code Snippet:
public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Vector v=new Vector();
v.add(10);
v.add(“Jyoti”);
v.add(15.2);
Enumeration e= v.elements();
while(e.hasMoreElements())
{
System.out.println(e.nextElement());
}
}
}
16. What are legacy classes in java?
In JDK 1.0 version java provides classes and interfaces in which we can store the data/Objects.
for e.g: Vector, Stack, Hashtable, Properties, Dictionary.
In JDK 1.2 version collection Framework was Introduced.
Legacy Classes:
Some classes i.e. Vector, Stack, Hashtable etc. was introduced in JDK 1.0 version but when collection framework was introduced in JDK 1.2 version these classes were modified or re-engineered so that they can be adjusted in new collection hierarchy, so these older classes are known as Legacy classes.
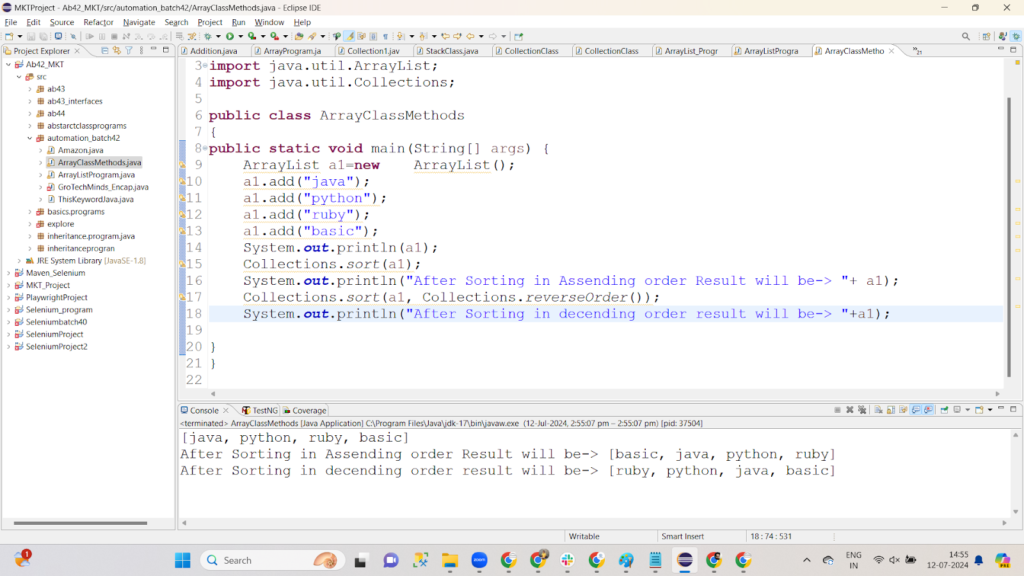
17. Demonstrate Java Collections sort and reverseorder methods.
Code Snippet:
package automation_batch42;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class ArrayClassMethods
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList a1=new ArrayList();
a1.add("java");
a1.add("python");
a1.add("ruby");
a1.add("basic");
System.out.println(a1);
Collections.sort(a1);
System.out.println("After Sorting in Ascending order Result will be-> "+ a1);
Collections.sort(a1, Collections.reverseOrder());
System.out.println("After Sorting in descending order result will be-> "+a1);
}
}
18. Does Collection class inherit Object Class?
Yes, the Object class is the root class of the entire class Hierarchy.
Also read:
Consult Us